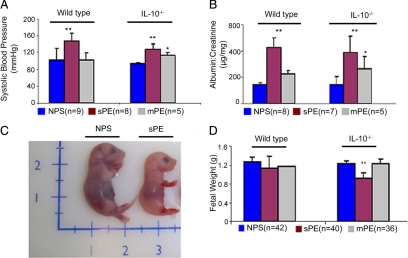
Figure 1.
Preeclampsia serum induces symptoms of hypertension, proteinuria, and IUGR in pregnant IL-10−/− mice. Pregnant wild-type or IL-10−/− mice were injected with normal pregnancy serum (NPS), severe preeclampsia serum (sPE), or mild preeclampsia serum (mPE) on gd 10. As depicted in the figure, multiple serum samples (parentheses) were used in multiple mating experiments. A: Systolic blood pressures of pregnant mice in response to different treatments are shown. Treatment with sPE (magenta bar) induces significant hypertension in both wild-type and IL-10−/− mice when compared with treatment with NPS (blue bar). Treatment with mPE (gray bar) induces moderate hypertension only in IL-10−/− mice compared with the NPS group. B: Proteinuria values from urine samples collected over 24-hour periods in response to different treatments are expressed as albumin to creatinine (microgram per milligram) ratios. Treatment with sPE (magenta bar) induces significant proteinuria in both wild-type and IL-10−/− mice compared with treatment with NPS (blue bar). Treatment with mPE (gray bar) induces moderate proteinura in IL-10−/− mice without significant effect in wild-type counterparts. C: A representative photograph of a gd 17 fetus shows sPE-induced growth restriction compared with that with NPS treatment. D: Average weights of a number of fetuses (n) from wild-type or IL-10−/− mice are represented for different treatment groups. Treatment with sPE (magenta bar), but not mPE (gray bar) or NPS (blue bar), induces IUGR in IL-10−/− mice with no significant effect in wild-type counterparts. All values represent the mean ± SD of at least seven animals per group. The numbers in parentheses indicate the number of serum samples tested in the study. *P < 0.01; **P < 0.05 for PE or normal pregnancy serum groups.