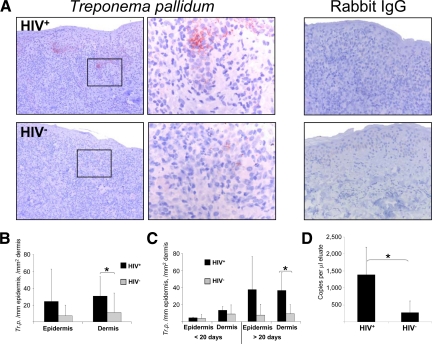
Figure 7.
Increase of T. pallidum in late secondary syphilitic lesions. A and B: Immunohistochemistry of paraffin sections with an anti–T. pallidum antibody shows an increase of treponemas in HIV-infected patients. Original magnification, ×100 of the total pictures and ×400 of the insets. B: Quantification of treponemas in the epidermis and dermis of syphilitic patients by immunohistochemistry. C: Further splitting of the samples to early and late secondary syphilitic lesions reveals that the increase of treponemas in HIV+ patients accounts only for late lesions of HIV-infected individuals. B and C: Data are given as the absolute numbers of treponemas ± SEM. *P < 0.05. D: Quantification of T. pallidum transcripts by quantitative RT-PCR. Data represent the mean values of copies per ml eluate ± SEM. *P < 0.05.