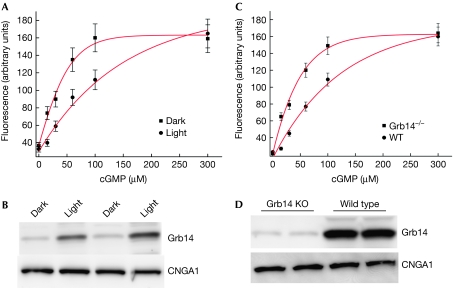
Figure 2.
Effect of growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 on cyclic guanosine monophosphate-mediated Ca2+ influx. (A) ROS (5 mg/ml) vesicles were prepared from dark- and light-adapted rats and the Fluo-3 dye was trapped inside them. Ca2+ influx was induced by the addition of cGMP (0–300 μM). (B) ROS membranes prepared from dark- and light-adapted animals were immunoblotted with Grb14 and CNGA1 antibodies. (C) ROS micelles prepared from Grb14−/− and wild-type mice were stimulated with cGMP (0–300 μM) and the increase in fluorescence triggered by Ca2+ influx into micelles was monitored. (D) ROS membranes from wild-type and Grb14−/− mice were subjected to immunoblot analysis with Grb14 and CNGA1 antibodies. The data are represented as mean±s.d., n=3 independent ROS micelles. cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; CNGA1, cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel alpha subunit; Grb14, growth factor receptor-bound protein 14; KO, knockout; ROS, rod outer segment.