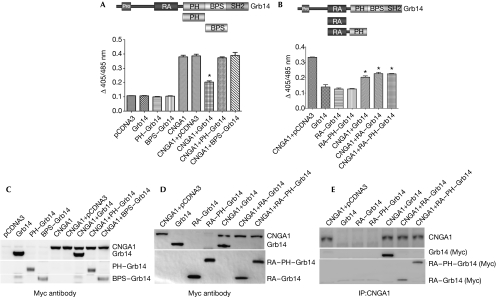
Figure 3.
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 modulates cyclic nucleotide-gated channel alpha subunit function through its Ras-associating domain. The domain organization of Grb14 is shown. CNGA1 was co-expressed (A) with the PH and BPS domains of Grb14 in HEK293T cells or (B) with the RA or RA–PH domains of Grb14 and examined for their effect on Ca2+ influx in response to cGMP. The data are represented as mean±s.d., n=3 independent transfections. Significance between CNGA1 and CNGA1 plus Grb14 or CNGA1 plus RA–Grb14 or RA–PH–Grb14, *P<0.001. Protein expression in cellular lysates was determined by immunoblotting with Myc antibody for (C) CNGA1, Grb14, PH–Grb14, BPS–Grb14 or (D) CNGA1, Grb14, RA–Grb14 or RA–PH–Grb14, respectively. (E) The physical interaction of the domains shown in (D) with CNGA1 was analysed by standard co-immunoprecipitation procedures using CNGA1 antibody. The immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with Myc antibody and reprobed with CNGA1 antibody. BPS, between the PH and SH2 domain; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; CNGA1, cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel alpha subunit; Grb14, growth factor receptor-bound protein 14; PH, Pleckstrin homology; RA, Ras-associating.