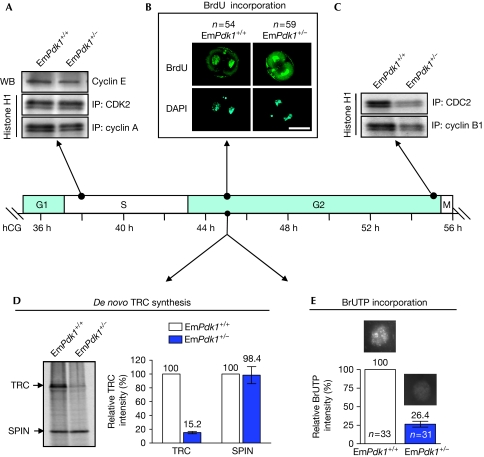
Figure 2.
Suppressed embryonic genome activation and defective G2/M phases in two-cell EmPdk1+/− embryos. Embryos were cultured for different lengths of time after hCG injection, corresponding to different stages of the second mitotic cell cycle. The arrows indicate time points when embryos were collected for different assays. (A) Levels of cyclin E and kinase activities of CDK2/cyclin A, showing the regular G1-to-S transition in two-cell EmPdk1+/− embryos. (B) Incorporation of BrdU into the nuclei, showing the completion of DNA synthesis in the indicated numbers (n) of EmPdk1+/+ and EmPdk1+/− embryos. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Kinase activities of CDC2/cyclin B1, showing the defective G2-to-M transition in EmPdk1+/− embryos. (D) Representative autoradiograph (left) and a histogram (right) showing the restrained TRC synthesis in EmPdk1+/− embryos at G2 phase. SPIN was the internal control. (E) Incorporation of BrUTP into the nuclei, showing the repression of global RNA synthesis in EmPdk1+/– embryos at G2 phase. Representative nuclei are shown above bars in the histogram. The number of nuclei analysed is denoted by n. BrdU, 5-bromo-2′deoxyuridine; BrUTP, 5-bromouridine-5′-triphosphate; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin; IP, immunoprecipitation; SPIN, spindlin; TRC, transcription-requiring complex; WB, western blot.