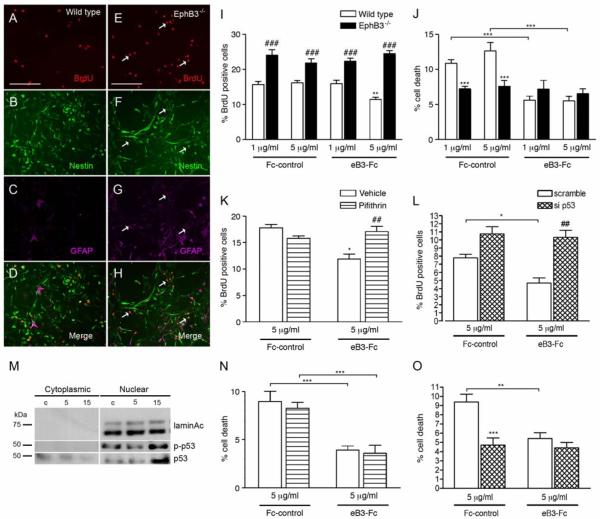
Figure 7.
EphB3 regulates proliferation of cultured SVZ-derived adult NSPCs in a p53-dependent manner. (A-D) Triple immunofluorescence labeling of BrdU-positive (red) wild type NSPCs with nestin (green) NSPC marker and GFAP (purple). EphB3−/− NSPCs have more proliferating nestin-expressing, GFAP-positive cells compared to wild type cultures. (I) Proliferation of wild type and EphB3−/− NSPCs in the presence and absence of soluble pre-clustered ephrinB3-Fc (eB3-Fc) and Fc-control (Fc). The percentage of BrdU-positive cells is increased in EphB3−/− cultures. The addition of 5 μg/ml eB3-Fc molecules for 3 days suppressed proliferation in wild type NSPCs compared to Fc-control, while having no effect in EphB3−/− cells. (J) The percentage of basal level cell death is reduced in EphB3−/− compared to wild type NSPCs. The addition of either 1 μg/ml or 5 μg/ml eB3-Fc reduced the percentage of cell death in wild type NSPCs compared to Fc-control, while having no effect in EphB3−/− cells. (K) EB3-Fc induced growth suppression (white bars) is attenuated in the presence of 10μM p53 inhibitor, Pifithrin compared to PBS-vehicle control. (L) Pre-treatment with si p53, 24 hours prior to stimulation also attenuated eB3-Fc induced growth suppression compared to siRNA scramble control. (M) EphB3 stimulation induces nuclear translocation of total p53 and phosphoSer15-p53 following 15 min eB3-Fc exposures compared to Fc-control (c). Inhibiting p53 with 10 μM Pifithrin (N) or si p53 (O) had no effect on altering the percentage of cell death in the presence of 5 μg/ml ephrinB3-Fc. (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared to corresponding wild type Fc-control; ###P<0.001 compared to wild type control in panel I and J), (*P<0.05 compared to Fc-control, ##P<0.01 compared to eB3-Fc plus vehicle in panel K, Scale bar = 200 μM).