Figure 1.
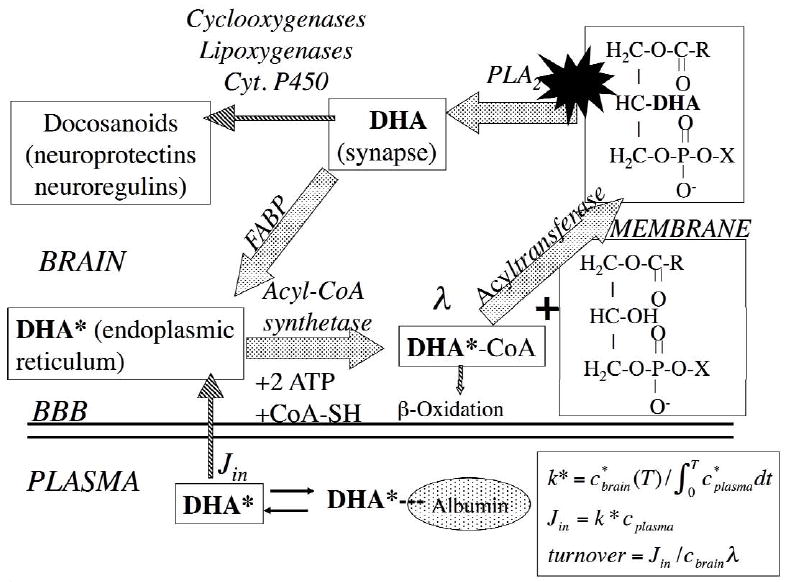
Brain docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) recycling at the synapse. DHA at the sn-2 position of a phospholipid is liberated by activation (star) of synaptic PLA2 at the synapse, secondary to neuroreceptor activation. A fraction of the unesterified DHA is converted to docosanoids, whereas the remainder is transported by a fatty acid binding protein (FABP) to the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is converted to DHA-CoA by an acyl-CoA synthetase, with the consumption of 2 ATPs. It then is esterified into an available lysophospholipid by an acyltransferase, or lost by β-oxidation in mitochondria or peroxisomes, or through other pathways (not shown). The brain unesterified DHA pool (not shown) rapidly exchanges with unesterified plasma DHA and labeled DHA*, which have dissociated from albumin. The DHA incorporation rate Jin equals the amount metabolized within brain and is calculated by equations in the right corner, where λ represents the ratio of DHA-CoA to plasma DHA specific activity. Modified from (12).
