Figure 4.
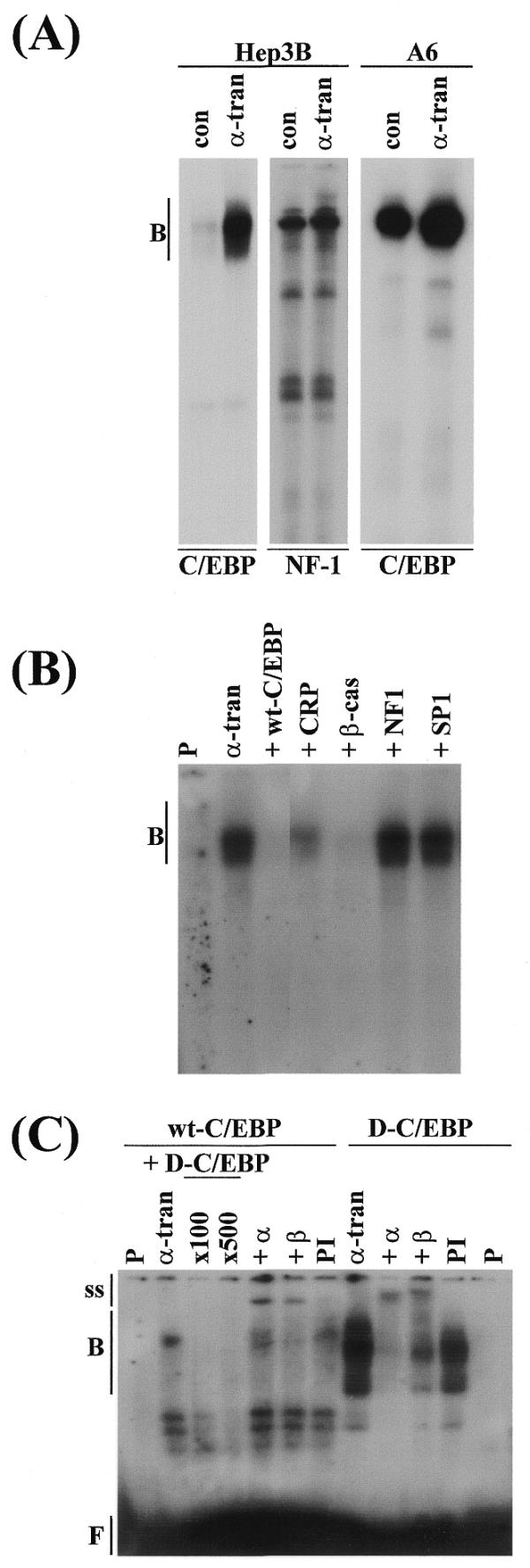
Interaction of the C/EBPs with the –218/–82 sequence. (A) Nuclear extracts from Hep3B or A6 cells, which had been transfected with the control pCS2+ vector (con) or the xC/EBPα expression plasmid (α-tran) were used for EMSA with radiolabelled wt-C/EBP or NF-1 binding site oligonucleotides. (B) Competition experiments were carried out using extracts from Hep3B cells transfected with the xC/EBPα expression plasmid and a 400-fold molar excess of oligonucleotides for: the corresponding unlabelled wt-C/EBP sequence (+wt-C/EBP), a C/EBP binding site from the C-reactive protein gene promoter (+CRP), a C/EBP binding site from the β-cas gene promoter (+β-cas), a NF-1 recognition sequence (+NF1) and a Sp1 binding site (+SP1). (C) Antibody interference EMSA was carried out using extracts from Hep3B cells transfected with the xC/EBPα expression plasmid and radiolabelled wt-C/EBP or D-C/EBP oligonucleotides, in the absence (α-tran) or the presence of antisera against C/EBPα (+α) or C/EBPβ (+β), or pre-immune serum (PI). For EMSA with wt-C/EBP oligonucleotide in (C), competition experiments were also carried out using a 100- and 500-fold molar excess of unlabelled D-C/EBP oligonucleotide (+D-C/EBP). Vertical arrows labelled B, ss and F indicate the position of the major DNA–protein complexes, antibody–DNA–protein supershifted complexes and free probe, respectively. P represents the profile obtained using the radiolabelled oligonucleotide alone; the free probe in (A) and (B) has migrated from the gel.
