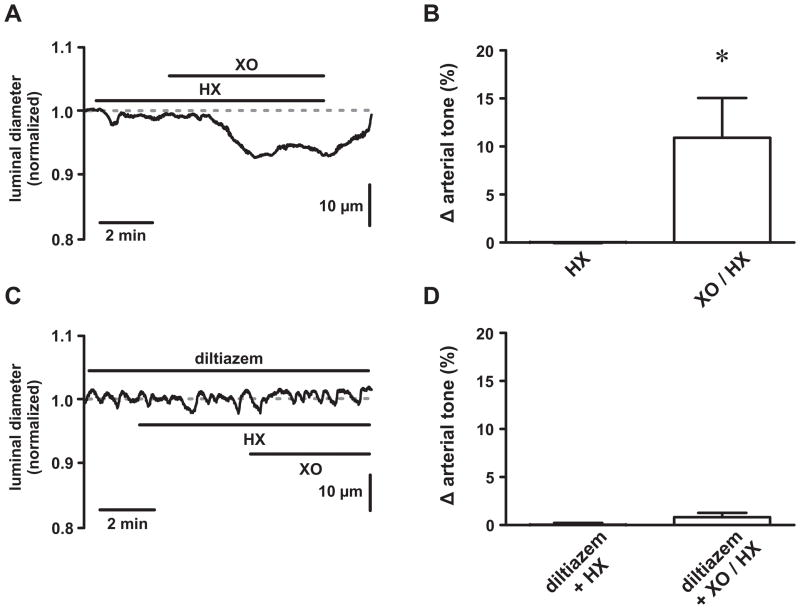
Figure 1. Reactive oxygen species increase tone in pressurized cerebral arteries.
A, Representative time course showing the luminal diameter of a pressurized (80 mm Hg) cerebral artery exposed to hypoxanthine (HX; 250 μmol/L) followed by xanthine oxidase (XO; 0.2mU/mL) plus HX. B, Plot of the mean ± SEM change in arterial tone (% Δ arterial tone) during HX and XO/HX exposure (n=7 arteries). C, Representative time course showing the luminal diameter of a pressurized (80 mm Hg) cerebral artery exposed to HX followed by XO/HX in the presence of the L-type Ca2+ channel blocker diltiazem (10 μmol/L). D, Plot of the mean ± SEM change in arterial tone (% Δ arterial tone) during diltiazem + HX and diltiazem + XO/HX exposure (n=3 arteries). *P<0.05