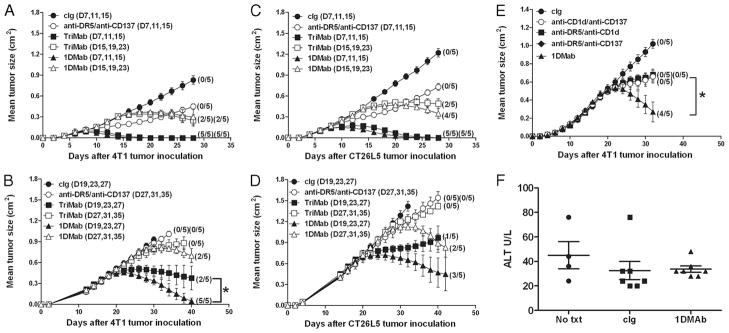
FIGURE 5.
1DMab therapy is more effective than TriMab therapy against established 4T1 and CT26L5 tumors. Groups of BALB/c mice (n = 5) were inoculated with either the mammary carcinoma cell line 4T1 (2 × 105; A, B, E, and F) or the colon carcinoma cell line CT26L5 (1 × 105; C and D). After tumor inoculation, mice were i.p. treated either with TriMab therapy (containing 200 μg of anti-CD40; ■ and □), 1DMab therapy (containing 200 μg of anti-CD1d; ▲ and △ ), or anti-DR5/anti-CD137 (○) or with cIg (●) at the time points indicated in parentheses. Statistical differences in survival between 1DMab-treated mice and TriMab-treated mice receiving the corresponding dose of anti-CD1d or anti-CD40 mAbs were determined by log-rank test (*, p < 0.05). E, On days 19, 23, and 27 after tumor inoculation groups of mice were treated with either 1DMab (▲), or anti-CD1d (200 μg)/anti-CD137 (○), or anti-DR5/anti-CD1d (200 μg; ■), or anti-DR5/anti-CD137 (◆), or cIg (●). Statistical differences in survival between mice treated with 1DMab or any two combinations of mAb from the 1DMab therapy were determined by log-rank test (*, p < 0.05). Tumor sizes are represented as the mean ± SEM of all mice and tumor rejection rates are indicated in parentheses. F, Serum was harvested 1 day later from untreated (No txt), cIg-treated, or 1DMab-treated mice bearing 4T1 tumors and alanine transferase (U/L) was measured. Results show the mean ± SEM of four mice per group.