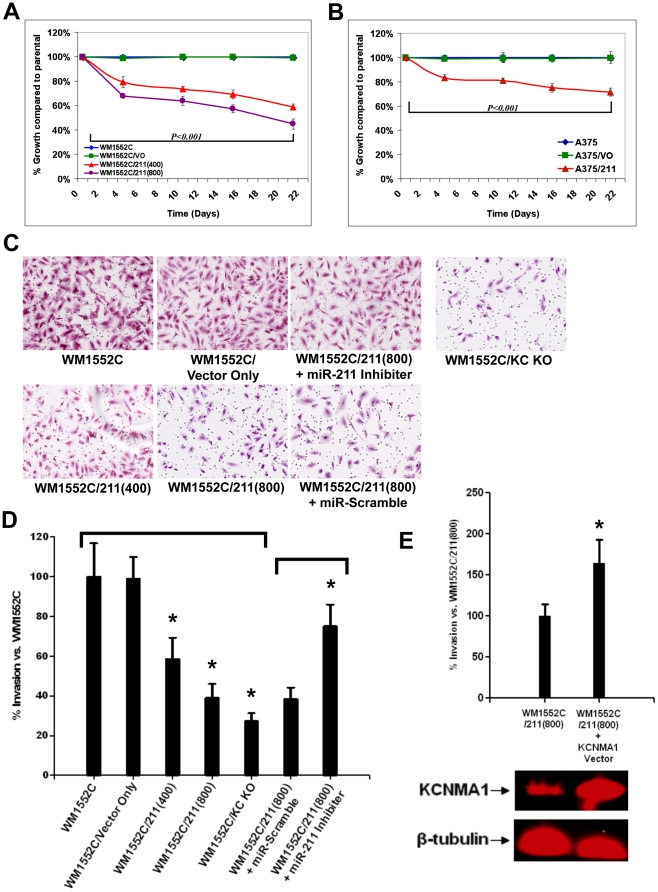
Figure 8. Effects of miR-211 over-expression on melanoma cells.
A and B: Relative mean cell titers of (A) WM1552C/211(400), WM1552C/211(800), and WM1552C/VO (vector only) cells to that of WM1552C cells and of (B) A375/211(400) and A375/VO (vector only) cells to that of A375 cells. (C) and (D): Cell invasion assays comparing WM1552C to WM1552C/VO, WM1552C/211(400), WM1552C/211(800), and WM1552C/KC KO stable derivatives, as well as to WM1552C/211(800) transfected with the Anti-miR miRNA Inhibiter for hsa-miR-211 [labelled “WM1552C/211(800) + miR-211”] or Negative Control #1 (labelled “WM1552C/211(800) + miR-Scramble”) over 48 hours. Each assay was performed in triplicate. Statistical significance is indicated by an asterisk in the figure pertaining to the experimental group delimited by a bar over the histograms (P-value<0.001). E) The artificial expression of KCNMA1 protein in WM1552C/211(800) cells increases melanoma cell invasiveness. Western blot results show that KCNMA1 protein levels are elevated in transfected cells [“WM1552C/211(800) + KCNMA1 Vector” relative to control cells without KCNMA1 expression vector] (bottom). β-tubulin was used as a load control. Results from the invasion assay illustrate that the KCNMA1 protein expression increased melanoma cell invasiveness (top).