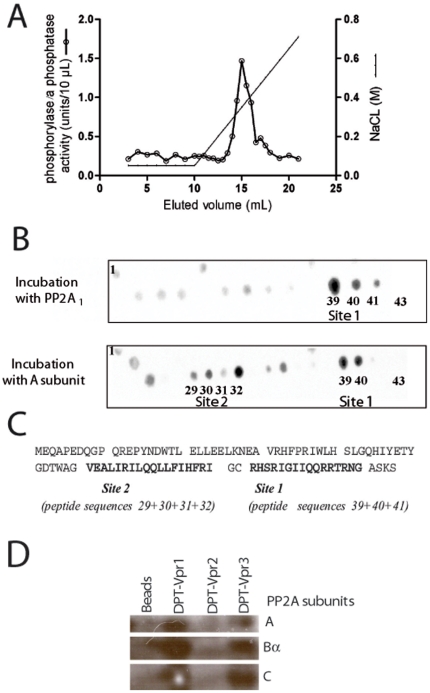
Figure 1. Analysis of HIV-1 Vpr and PP2A1 interaction.
(A) 16 µg of PP2A1 holoenzyme purified from pig brain was loaded on a 1 mL HIV-1 strain 89.6-Vpr-T-agarose column equilibrated in buffer C (25 mM TrisHCl pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA). The column was washed with 10 mL of buffer C and then developed with a 18 mL linear gradient of buffer C to buffer C plus 1 M NaCl. Phosphatase activity of collected fractions was assayed with phosphorylase a as substrat (1U = 1 pm of phosphate liberated by 10 µL of fraction/min). A major peak of phosphatase activity was detected, eluting at 0.3 M NaCl. (B) ECL revelation of PP2A binding assay on cellulose-bound Vpr peptides. 43 overlapping dodecapeptides with a two-amino acid shift scanning the entire 89.6-Vpr sequence (accession number: AAA81039) were synthesized on a cellulose membrane. The membrane was incubated with PP2A1 holoenzyme (upper panel) or PP2A-A subunit (lower panel) and subsequently with anti-PP2A antibodies followed by peroxydase-labelled anti-guinea pig antibodies. (C) Sequence of HIV-1 Vpr protein: sequence of the two PP2A-A binding sites are indicated in bold. These sequences correspond to overlapping sequences of positive dodecapeptides 29 to 32 (PP2A-A subunit incubation) or 39 to 41 (PP2A1 incubation). (D) Co-precipitation of DPT-Vpr peptides with PP2A1 in HeLa cell extracts. Control magnetic beads coupled with streptavidin alone or conjugated with DPT-Vpr peptides at a concentration of 100 µM, were incubated with cells extracts (5.105 cells). Identification of bound proteins in pull-down experiments was realized by immunoblotting using antibodies against PP2A1 subunits A, Bα and C.