Figure 6.
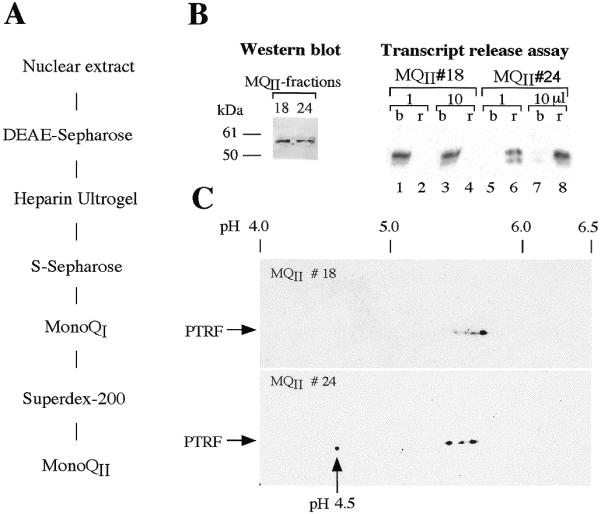
Charge heterogeneity of active and inactive forms of PTRF. (A) Diagram showing the chromatographic steps used to purify PTRF from nuclear extracts. (B) Chromatographic separation of release-competent and -incompetent forms of PTRF. Individual fractions from the last purification step, e.g., Mono QII, were analyzed on western blots or assayed for their capability to dissociate ternary transcription complexes. Ternary complexes were formed by pre-incubating bead-bound tailed template (pCAT-T6-T1) for 5 min with Pol I, TTF-I and nucleotides to allow Pol I to reach the terminator. Paused complexes were removed by magnetic attraction, washed with buffer AM-200, and then incubated for another 5 min with cold nucleotides in the presence of fractions MQII #18 and #24, respectively. Transcripts were separated into template-bound (b) and released (r) fractions. 2D gel electrophoresis of fractions MQII #18 and #24. The two fractions were subjected to 2D gel electrophoresis, blotted onto nitrocellulose filters, and PTRF was immunostained with anti-PTRF antibodies.
