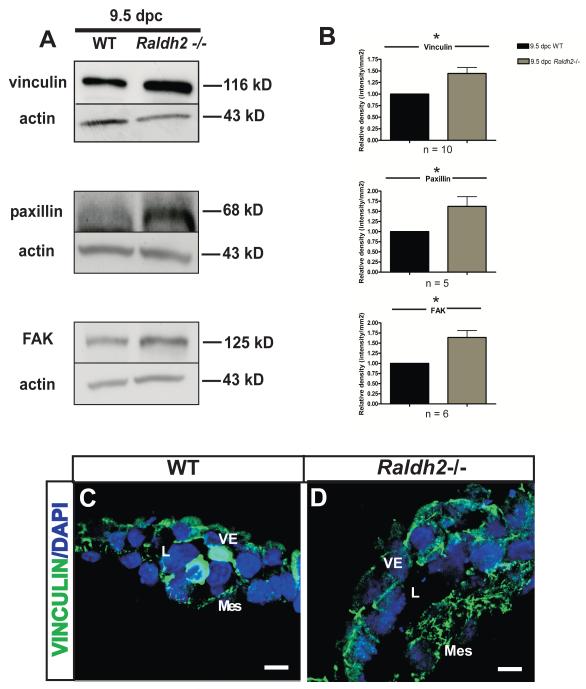
Figure 3. Focal adhesions are increased in Raldh2−/− mutants that fail to undergo vascular remodeling.
(A) Representative Western blots are shown that demonstrate increased protein levels of the focal adhesion proteins vinculin, paxillin, and FAK in Raldh2−/− yolk sacs versus WT yolk sacs at 9.5 dpc. Actin was used as the loading control. (B) Quantitation of Western blots for vinculin, paxillin, and FAK is represented by bar graphs indicating the mean band density +/− SEM measured for Raldh2−/− mutants relative to WT for each focal adhesion protein. Vinculin (p = 0.0027), paxillin (p = 0.032), and FAK (p = 0.0036) were significantly increased in Raldh2−/− yolk sacs as determined by a two-tailed student t-test (*p ≤ 0.05 as denoted by an asterisk; n = number of independent Western blot experiments repeated for each focal adhesion protein). Representative fluorescence confocal images are shown which demostrate the localization of vinculin (green) in WT (C) and Raldh2−/− yolk sacs (D). Vinculin expression is increased in the cytoplasm of yolk sac mesodermal cells and endoderm cell-cell borders at 9.5 dpc in Raldh2−/− mutants compared to WT. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). VE = visceral endoderm; Mes = mesoderm; L = blood vessel lumen; scale bars = 10 μm.