Figure 2.
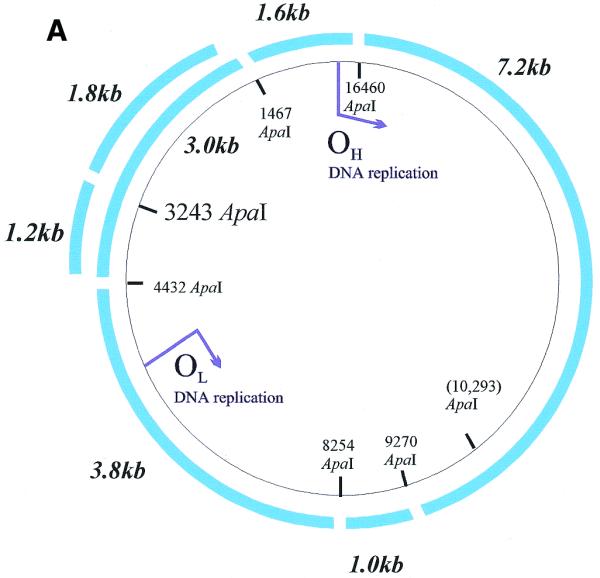
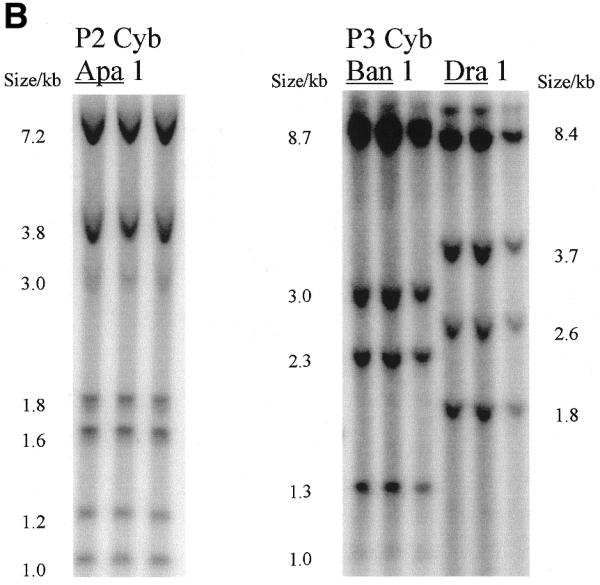
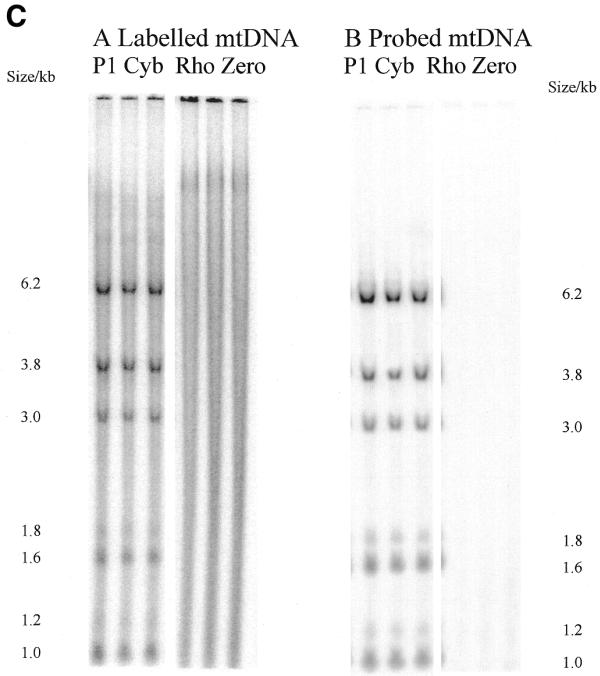
Radioactivity is incorporated into wild-type and A3243G mutant mtDNA and corresponding steady-state mtDNA. (A) Map of human mtDNA to show ApaI restriction sites. ApaI restriction sites and sizes of the fragments generated are indicated. The polymorphic site in line P1 cyb is in brackets. The additional fragments generated when the heteroplasmic 3243 mutation is present are shown outside the wild-type fragments. Origins of DNA replication OH and OL are marked with arrows. (B) Southern blot of labelled mtDNA digested with various restriction enzymes. DNA from patient-derived cell lines P2 cyb and P3 cyb was extracted after pulse labelling in the presence of 5 mg/ml aphidicolin to inhibit nuclear replication. Restriction by ApaI, BanI and DraI all resulted in the predicted restriction fragments for mtDNA. In addition, the A3243G mutation introduces an ApaI restriction site so that the 3 kb band is replaced by bands of 1.2 and 1.8 kb. (C) Comparison of Southern blotted, labelled and probed mtDNA from a patient-derived cybrid and a mtDNA-free cell line. (Left) Phosphorimage of a filter with Southern blotted labelled DNA from a permeabilised cell assay using DNA from patient-derived cell line P1 cyb and a ρ0 line cut with restriction enzyme ApaI. (Right) The same filter probed with a full-length mtDNA probe. Both resulted in the predicted restriction fragments for mtDNA in the patient-derived line which are absent from the ρ0 line. Cell line P1 cyb has an additional ApaI site which maps to base pair 10 293, so that a 6.2 kb band replaces the 7.2 kb band and the 1 kb ApaI band represents two co-migrating fragments.
