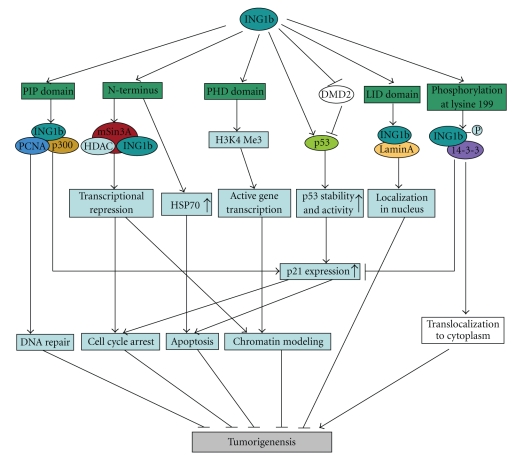
Figure 2.
The role of p33ING1b protein in tumor supression. p33ING1b could recognize trimethylated lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4me3) by PHD domain and has been implicated in chromatin remodeling and activation of some genes transcription. This binding is somehow necessary for induction of DNA repair and cell death. p33ING1b also associates with the Sin3/HDAC-mediated transcriptional repression through its unique N-terminal sequence and may be involved in repression of some essential cell cycle regulator genes. Moreover, p33ING1b binds PCNA and p300 complex to promote DNA repair through a PIP motif in response to UV-irradiation and, subsequently, may trigger apoptosis by the induction of p21 expression. p33ING1b competes with murine double minute 2 (MDM2) leading to an increase in the stability and activity of p53. p21, the one of the targets of p53, is also upregulated to involve in cell cycle arrest and the induction of apoptosis. Additionally, p33ING1b could upregulate expression of HSP70 gene to induce apoptosis independently of p53 status. Furthermore, p33ING1b binds to lamin A via LID domain to stabilize its level and biological function in nucleus. Conversely, 14-3-3 can bind to p33ING1b with phosphorylated serine 199 and results in translocation of p33ING1b from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, which may involve in tumorigenesis.