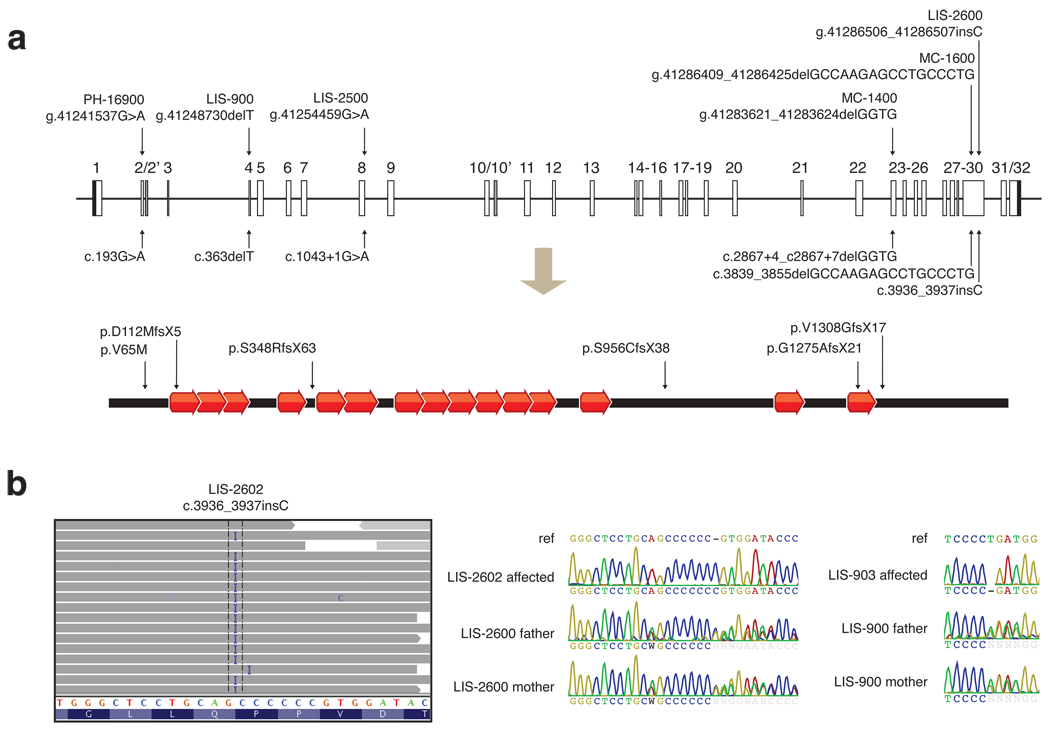
Figure 3.
Six WDR62 mutations reported in association with microcephaly with simplified gyri. (a) Alterations are shown in genomic, coding DNA, and protein contexts. The human WDR62 gene consists of 32 exons shown as boxes, and encodes a protein of 1518 amino acids containing 15 WD40 repeats. Black shaded boxes represent untranslated regions, open boxes represent coding regions, and gray shaded boxes represent alternatively spliced exons. Lines connecting boxes represent introns. The diagram is drawn to scale. Five of the six alleles (from families LIS-900, LIS-2500, LIS-2600, MC-1400, MC-1600, and LIS-2600) disrupt splice sites or cause frameshifts resulting in protein truncations and are likely nulls. The sixth allele, found in PH-16900, is a missense alteration of V65M, a conserved residue. (b) Illustration of the c.3936_3937insC mutation in LIS-2602 by high throughput sequencing, and representative Sanger traces confirming proper segregation. High throughput sequencing data is shown using the Integrated Genome Viewer. Aligned reads are shown as gray tags shaded by quality score, SNPs are identified by the letter code of the substituted base, and the position of the LIS-2602 single basepair insertion is denoted by the letter I. Representative Sanger traces confirm this change in the affected individual and show that both parents are heterozygous for the insertional event. Similarly, representative Sanger traces illustrate the c.363delT mutation in LIS-903 and the carrier status of both parents.