Figure 5. Reduced Tether Stability in bubR1 and polo Mutants.
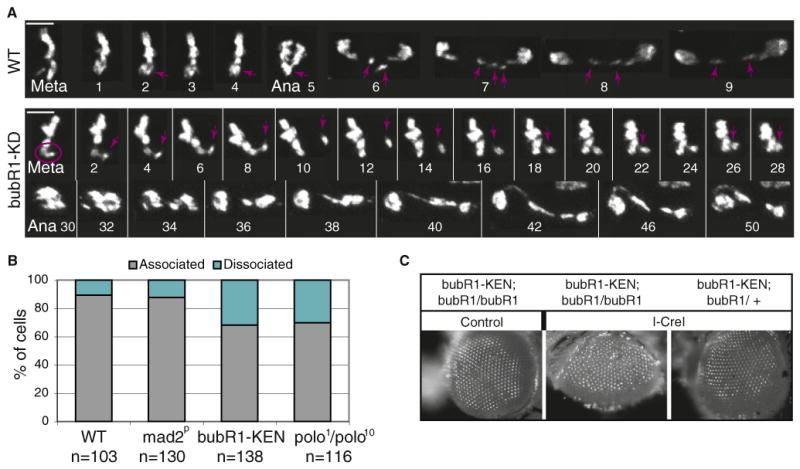
(A) Time-lapse imaging of mitotic GFP-H2Av-labeled neuroblasts from wild-type and bubR1-KD mutant larvae expressing I-CreI. In the wild-type, the acentrics align at the metaphase plate and segregate toward each pole during anaphase (purple arrow). In the bubR1-KD mutant, we observe instances in which the acentric (purple circle) is associated with the main chromosome mass, and then detaches and migrates away (purple arrow). The acentric eventually reassociates with the chromosome mass. Anaphase is triggered soon after but is abnormal. Time is presented as min:s. The scale bar represents 5 μm.
(B) Frequency of acentrics that are associated or dissociated from their centric partners. The quantification was done as described in Figure 2C. n = number of neuroblasts. Neuroblasts were scored in two independent experiments for each genotype (two to four brains per experiment).
(C) Images of adult eyes from bubR1-KEN mutant, homozygote (bubR1/bubR1), or heterozygote (bubR1/CyO) for bubR11 with (I-CreI) or without (control) the I-CreI transgene. The third-instar larvae were heat shocked and allowed to develop into adults. Note the roughness of the eye of bubR1-KEN mutant after I-CreI induction suggesting a loss of omatidia during development.
