Abstract
In the title compound, C21H17N5·H2O, the dihedral angles between the acridine ring system and the imidazole rings are 78.8 (1) and 71.2 (1)°. The crystal packing is stabilized by O—H⋯N, C—H⋯O, C—H⋯π and π–π interactions [centroid–centroid separations = 3.732 (1) and 3.569 (1) Å].
Related literature
For the biological activity of acridines, see: Talacki et al. (1974 ▶); Achenson (1956 ▶); Prasad Krishna et al. (1984 ▶); Asthana et al. (1991 ▶). For their antiprotozoal activity, see: Karolak-Wojciechowska et al. (1996 ▶). For the ability of acridine to intercalate between the base-pairs of DNA, see: Neidle (1979 ▶); Fan et al. (1997 ▶). For acridine compounds in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, see: Bandoli et al. (1994 ▶). For their toxicity, see: Di Giorgio et al. (2005 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H17N5·H2O
M r = 357.41
Monoclinic,

a = 14.3359 (6) Å
b = 6.9132 (3) Å
c = 17.7458 (8) Å
β = 92.895 (3)°
V = 1756.49 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.25 × 0.22 × 0.19 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.978, T max = 0.984
19520 measured reflections
4286 independent reflections
2652 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.036
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.145
S = 1.06
4286 reflections
252 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903267X/bt5021sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903267X/bt5021Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C18—H18B⋯O1i | 0.97 | 2.55 | 3.482 (3) | 162 |
| O1—H1A⋯N3 | 0.90 (3) | 2.07 (3) | 2.945 (3) | 166 (3) |
| O1—H1B⋯N5ii | 0.85 (3) | 2.21 (3) | 3.030 (3) | 162 (3) |
| C7—H7⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.69 | 3.577 (2) | 159 |
| C20—H20⋯Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.648 (2) | 139 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  . Cg1 is the centroid of the N4/N5/C19–C21 ring.
. Cg1 is the centroid of the N4/N5/C19–C21 ring.
Acknowledgments
ST and ASP thank Dr Babu Varghese, SAIF, IIT, Chennai, India, for the X-ray data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Acridines are found to have a wide range of biological activities, such as mutagenic, antitumour (Talacki et al., 1974), antibacterial (Achenson, 1956), antiamoebic (Prasad Krishna et al., 1984), hypersensitive, antiinflammatory and antiimplantation (Asthana et al., 1991) activities. A drug containing the acridine moiety has been found to possess antiprotozoal activity (Karolak-Wojciechowska et al., 1996). The ability of acridine to intercalate between the base-pairs of DNA is also well known (Neidle, 1979; Fan et al., 1997). Acridine compounds are considered to be efficient drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (Bandoli et al., 1994). Acridine derivatives have been shown to exert toxicity towards Plasmodium, Trypanosoma, and Leishmania parasites (Di Giorgio et al., 2005). The imidazole group have found a wide range of applications in coordination chemistry as ligands, in medicinal chemistry and materials science. Against this background, and in order to obtain detailed information on molecular conformations in the solid state, an X-ray study of the title compound has been carried out.
The two imidazole groups are almost parallel to each other, the dihedral angle between the mean planes being 39.5 (1)°; these planes are inclined at 78.9 (1)° and 71.2 (9)° with respect to the mean plane of the acridine system. The pseudo-torsion angle N2–C14···.C18–N4 [-145.8 (2)°], resulting in both imidazole group being approximately bisected by the plane of the acridine system. The acridine ring system and imidazole rings are essentially planar, with maximum deviations of 0.062 (3), 0.006 (2) and 0.001 (2) Å, for atoms C4, N3 and C19, respectively.
The crystal packing is stabilized by C–H···O, C–H···N, C–H···π (Table. 1) and π–π interactions with a Cg2···Cg2ii and a Cg4···Cg3iv separation of 3.732 (1)Å and 3.569 (1) Å, respectively (Fig.2; Cg2, Cg3 and Cg4 are the centroids of the N2/N3/C15–C17 imidazole ring, N1/C1/C6/C7/C8/C13 pyridine ring and C8–C13 benzene ring, respectively, symmetry code as in Fig. 2).
Experimental
To a solution of imidazole, in the presence of acetonitrile (50 ml) and NaOH solution (7.5 ml) was added and stirred for 10 minutes, then 4,5-bis(bromomethyl) acridine in the presence of acetonitrile(20 ml) was added at once and stirred at room temperature for 48hrs. After completion of reaction, the solvent was evaporated in vaccum and the residue was extracted with CHCl3(300 ml). Single crystals suitable for the X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution of the title compound in methanol at room temperature.
Refinement
H atoms of water were located is a difference fourier map, and were refined with distance restraints of O–H= 0.85 (3)Å. All other H atoms were fixed geometrically and allowed to ride on their parent atoms, with C–H = 0.93–0.98Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C, N).
Figures
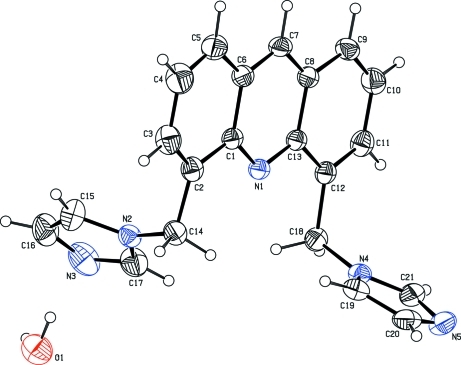
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme and intramolecular hydrogen bond. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
C–H···O, O–H···N, C–H···π and π—π interactions (dotted lines) in the title compound. Cg denotes ring centroid. [Symmetry code: (i) -1/2 - x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 - z; (ii) -x, 1 - y, -z; (iii) 1 - x, 2 - y, -z; (iv) 1 - x, 1 - y, -z; (v) 1/2 - x, 2 - y, -z]
Crystal data
| C21H17N5·H2O | F(000) = 752 |
| Mr = 357.41 | Dx = 1.352 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 4286 reflections |
| a = 14.3359 (6) Å | θ = 1.8–28.1° |
| b = 6.9132 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 17.7458 (8) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 92.895 (3)° | Block, white crystalline |
| V = 1756.49 (13) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.22 × 0.19 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4286 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2652 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.036 |
| ω scans | θmax = 28.1°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −19→19 |
| Tmin = 0.978, Tmax = 0.984 | k = −9→8 |
| 19520 measured reflections | l = −23→23 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.145 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0577P)2 + 0.3961P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4286 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 252 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.31970 (12) | 0.7854 (2) | −0.06027 (9) | 0.0394 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.22370 (12) | 0.8010 (3) | −0.08514 (10) | 0.0463 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.20069 (15) | 0.8387 (3) | −0.15855 (12) | 0.0618 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.1382 | 0.8558 | −0.1737 | 0.074* | |
| C4 | 0.26910 (17) | 0.8528 (4) | −0.21250 (12) | 0.0715 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.2513 | 0.8793 | −0.2626 | 0.086* | |
| C5 | 0.35988 (16) | 0.8283 (3) | −0.19224 (11) | 0.0609 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.4041 | 0.8324 | −0.2288 | 0.073* | |
| C6 | 0.38899 (13) | 0.7960 (3) | −0.11539 (10) | 0.0446 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.48111 (13) | 0.7751 (3) | −0.09095 (10) | 0.0466 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.5274 | 0.7779 | −0.1258 | 0.056* | |
| C8 | 0.50554 (12) | 0.7500 (2) | −0.01541 (10) | 0.0414 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.59945 (12) | 0.7289 (3) | 0.01289 (12) | 0.0509 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.6476 | 0.7313 | −0.0203 | 0.061* | |
| C10 | 0.61933 (13) | 0.7056 (3) | 0.08691 (12) | 0.0570 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.6811 | 0.6912 | 0.1048 | 0.068* | |
| C11 | 0.54661 (13) | 0.7027 (3) | 0.13806 (11) | 0.0522 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.5617 | 0.6857 | 0.1892 | 0.063* | |
| C12 | 0.45576 (12) | 0.7241 (2) | 0.11476 (10) | 0.0412 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.43189 (11) | 0.7464 (2) | 0.03633 (9) | 0.0374 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.14924 (12) | 0.7687 (3) | −0.03008 (11) | 0.0490 (4) | |
| H14A | 0.1671 | 0.8318 | 0.0173 | 0.059* | |
| H14B | 0.0912 | 0.8261 | −0.0496 | 0.059* | |
| C15 | 0.10166 (15) | 0.4321 (3) | −0.06850 (13) | 0.0663 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.0865 | 0.4554 | −0.1193 | 0.080* | |
| C16 | 0.09479 (17) | 0.2638 (3) | −0.03245 (16) | 0.0750 (7) | |
| H16 | 0.0727 | 0.1496 | −0.0545 | 0.090* | |
| C18 | 0.38042 (13) | 0.7272 (3) | 0.17082 (10) | 0.0465 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.3235 | 0.6737 | 0.1474 | 0.056* | |
| H18B | 0.3992 | 0.6459 | 0.2135 | 0.056* | |
| C19 | 0.30224 (12) | 1.0562 (3) | 0.16560 (11) | 0.0497 (5) | |
| H19 | 0.2643 | 1.0415 | 0.1219 | 0.060* | |
| C20 | 0.30963 (14) | 1.2133 (3) | 0.20991 (12) | 0.0584 (5) | |
| H20 | 0.2765 | 1.3275 | 0.2013 | 0.070* | |
| C21 | 0.40165 (14) | 1.0055 (3) | 0.25943 (10) | 0.0554 (5) | |
| H21 | 0.4454 | 0.9443 | 0.2917 | 0.067* | |
| N1 | 0.34184 (9) | 0.76245 (19) | 0.01343 (8) | 0.0385 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.13497 (9) | 0.5626 (2) | −0.01681 (8) | 0.0446 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.12452 (15) | 0.2830 (3) | 0.04082 (14) | 0.0815 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.36165 (9) | 0.9226 (2) | 0.19781 (8) | 0.0427 (4) | |
| N5 | 0.37208 (13) | 1.1834 (3) | 0.26923 (10) | 0.0658 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.04120 (12) | 0.0382 (3) | 0.15544 (11) | 0.0766 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.14712 (15) | 0.4659 (4) | 0.04758 (12) | 0.0668 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.1693 | 0.5221 | 0.0926 | 0.080* | |
| H1A | 0.074 (2) | 0.096 (5) | 0.120 (2) | 0.138 (14)* | |
| H1B | 0.066 (2) | −0.070 (4) | 0.1662 (16) | 0.099 (11)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0282 (9) | 0.0424 (9) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0082 (7) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0493 (10) | 0.0365 (10) | 0.0527 (11) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0009 (8) | 0.0019 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0616 (12) | 0.0634 (14) | 0.0593 (12) | −0.0044 (10) | −0.0090 (10) | 0.0072 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0830 (16) | 0.0837 (18) | 0.0469 (12) | −0.0154 (13) | −0.0069 (11) | 0.0117 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0765 (14) | 0.0628 (14) | 0.0444 (11) | −0.0136 (11) | 0.0120 (10) | 0.0034 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0534 (10) | 0.0353 (10) | 0.0459 (10) | −0.0060 (7) | 0.0119 (8) | −0.0001 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0533 (10) | 0.0383 (10) | 0.0501 (10) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0206 (8) | −0.0025 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0435 (9) | 0.0277 (9) | 0.0539 (10) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0115 (7) | −0.0023 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0434 (9) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0681 (13) | 0.0009 (8) | 0.0150 (8) | −0.0049 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0434 (10) | 0.0515 (13) | 0.0756 (14) | 0.0053 (8) | −0.0005 (9) | −0.0052 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0560 (11) | 0.0450 (12) | 0.0548 (11) | 0.0033 (8) | −0.0039 (9) | −0.0028 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0468 (9) | 0.0302 (9) | 0.0469 (10) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0044 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0419 (9) | 0.0255 (8) | 0.0456 (9) | 0.0006 (6) | 0.0082 (7) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0443 (9) | 0.0406 (11) | 0.0623 (12) | 0.0026 (8) | 0.0027 (8) | −0.0001 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0788 (14) | 0.0549 (14) | 0.0635 (13) | −0.0027 (11) | −0.0115 (11) | −0.0049 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0743 (15) | 0.0424 (13) | 0.108 (2) | −0.0039 (10) | 0.0035 (14) | −0.0016 (13) |
| C18 | 0.0569 (10) | 0.0406 (11) | 0.0423 (9) | −0.0052 (8) | 0.0057 (8) | 0.0042 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0440 (9) | 0.0541 (12) | 0.0519 (10) | 0.0030 (8) | 0.0122 (8) | 0.0075 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0586 (12) | 0.0549 (13) | 0.0642 (13) | 0.0068 (9) | 0.0276 (10) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C21 | 0.0568 (11) | 0.0655 (14) | 0.0445 (10) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0071 (8) | −0.0060 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0420 (7) | 0.0303 (8) | 0.0440 (8) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0090 (6) | −0.0001 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0398 (7) | 0.0426 (9) | 0.0516 (9) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0018 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0780 (13) | 0.0672 (15) | 0.0993 (17) | −0.0087 (10) | 0.0051 (12) | 0.0298 (12) |
| N4 | 0.0448 (8) | 0.0454 (9) | 0.0388 (7) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0111 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
| N5 | 0.0769 (12) | 0.0624 (13) | 0.0598 (11) | −0.0014 (9) | 0.0203 (9) | −0.0158 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0682 (10) | 0.0828 (14) | 0.0784 (12) | 0.0017 (10) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0099 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0725 (14) | 0.0716 (17) | 0.0562 (12) | −0.0135 (12) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0141 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—N1 | 1.340 (2) | C14—N2 | 1.460 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.428 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.431 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.353 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.334 (3) |
| C2—C14 | 1.500 (2) | C15—N2 | 1.356 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.408 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C16—N3 | 1.354 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.343 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C18—N4 | 1.462 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.423 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.377 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.342 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.379 (3) | C19—N4 | 1.362 (2) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.421 (3) | C20—N5 | 1.363 (3) |
| C8—C13 | 1.434 (2) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.340 (3) | C21—N5 | 1.315 (3) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C21—N4 | 1.338 (2) |
| C10—C11 | 1.416 (3) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | N2—C17 | 1.327 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.355 (2) | N3—C17 | 1.310 (3) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9300 | O1—H1A | 0.91 (4) |
| C12—C13 | 1.425 (2) | O1—H1B | 0.85 (3) |
| C12—C18 | 1.505 (2) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C13—N1 | 1.338 (2) | ||
| N1—C1—C2 | 119.20 (15) | N2—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| N1—C1—C6 | 122.36 (15) | C2—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.44 (16) | N2—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.77 (17) | C2—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C3—C2—C14 | 120.60 (17) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.0 |
| C1—C2—C14 | 119.60 (16) | C16—C15—N2 | 106.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.58 (19) | C16—C15—H15 | 126.6 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.2 | N2—C15—H15 | 126.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C15—C16—N3 | 110.4 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.52 (19) | C15—C16—H16 | 124.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | N3—C16—H16 | 124.8 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | N4—C18—C12 | 112.31 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.63 (19) | N4—C18—H18A | 109.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C12—C18—H18A | 109.1 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | N4—C18—H18B | 109.1 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 123.26 (17) | C12—C18—H18B | 109.1 |
| C7—C6—C1 | 117.86 (16) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.9 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.88 (17) | C20—C19—N4 | 105.90 (18) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.78 (15) | C20—C19—H19 | 127.1 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.6 | N4—C19—H19 | 127.1 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.6 | C19—C20—N5 | 111.03 (19) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 123.10 (16) | C19—C20—H20 | 124.5 |
| C7—C8—C13 | 117.74 (15) | N5—C20—H20 | 124.5 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 119.16 (16) | N5—C21—N4 | 112.40 (19) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.65 (17) | N5—C21—H21 | 123.8 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.7 | N4—C21—H21 | 123.8 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.7 | C13—N1—C1 | 118.91 (14) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.20 (18) | C17—N2—C15 | 105.89 (18) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.9 | C17—N2—C14 | 128.06 (17) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.9 | C15—N2—C14 | 125.97 (17) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 122.02 (18) | C17—N3—C16 | 104.28 (19) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.0 | C21—N4—C19 | 106.58 (17) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.0 | C21—N4—C18 | 125.81 (16) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.33 (16) | C19—N4—C18 | 127.60 (15) |
| C11—C12—C18 | 120.72 (16) | C21—N5—C20 | 104.10 (17) |
| C13—C12—C18 | 119.95 (15) | H1A—O1—H1B | 109 (3) |
| N1—C13—C12 | 119.07 (14) | N3—C17—N2 | 112.7 (2) |
| N1—C13—C8 | 122.30 (15) | N3—C17—H17 | 123.6 |
| C12—C13—C8 | 118.62 (15) | N2—C17—H17 | 123.6 |
| N2—C14—C2 | 111.13 (14) | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 175.05 (17) | C9—C8—C13—N1 | −178.93 (15) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −4.7 (3) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | −178.90 (15) |
| N1—C1—C2—C14 | −7.0 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 0.8 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C14 | 173.28 (16) | C3—C2—C14—N2 | 99.4 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 3.6 (3) | C1—C2—C14—N2 | −78.6 (2) |
| C14—C2—C3—C4 | −174.4 (2) | N2—C15—C16—N3 | −1.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.2 (4) | C11—C12—C18—N4 | 89.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.8 (4) | C13—C12—C18—N4 | −89.38 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.2 (2) | N4—C19—C20—N5 | 0.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.5 (3) | C12—C13—N1—C1 | 179.31 (14) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | 2.2 (2) | C8—C13—N1—C1 | −1.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.12 (16) | C2—C1—N1—C13 | 179.48 (15) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −177.52 (17) | C6—C1—N1—C13 | −0.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 2.2 (2) | C16—C15—N2—C17 | 0.5 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 177.98 (18) | C16—C15—N2—C14 | −176.70 (17) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −1.7 (3) | C2—C14—N2—C17 | 118.2 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −179.63 (16) | C2—C14—N2—C15 | −65.3 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C13 | 0.0 (2) | C15—C16—N3—C17 | 1.3 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.76 (18) | N5—C21—N4—C19 | 0.1 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.1 (3) | N5—C21—N4—C18 | 179.16 (15) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.3 (3) | C20—C19—N4—C21 | −0.08 (19) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.4 (3) | C20—C19—N4—C18 | −179.16 (15) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 1.3 (3) | C12—C18—N4—C21 | −92.4 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12—C18 | −177.90 (18) | C12—C18—N4—C19 | 86.5 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13—N1 | 178.27 (15) | N4—C21—N5—C20 | 0.0 (2) |
| C18—C12—C13—N1 | −2.6 (2) | C19—C20—N5—C21 | 0.0 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13—C8 | −1.4 (2) | C16—N3—C17—N2 | −1.0 (3) |
| C18—C12—C13—C8 | 177.73 (15) | C15—N2—C17—N3 | 0.4 (3) |
| C7—C8—C13—N1 | 1.4 (2) | C14—N2—C17—N3 | 177.43 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C18—H18B···O1i | 0.97 | 2.55 | 3.482 (3) | 162 |
| O1—H1A···N3 | 0.90 (3) | 2.07 (3) | 2.945 (3) | 166 (3) |
| O1—H1B···N5ii | 0.85 (3) | 2.21 (3) | 3.030 (3) | 162 (3) |
| C7—H7···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.69 | 3.577 (2) | 159 |
| C20—H20···Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.648 (2) | 139 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1/2, y−3/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x+1, −y+2, −z; (iv) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5021).
References
- Achenson, R. M. (1956). In Acridines: The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, Vol. 9, edited by A. Weissberger, pp. 339–361. New York: Interscience.
- Asthana, P., Rastogi, S., Ghose, S. & Das, S. R. (1991). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 30, 893–900.
- Bandoli, G., Dolmella, A., Gatto, S. & Nicolini, M. (1994). J. Chem. Crystallogr.24, 301–310.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Di Giorgio, C., De Meo, M., Chiron, J., Delmas, F., Nikoyan, A., Severine, J., Dumenil, G., Timon-David, P. & Galy, J.-P. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem.13, 5560–5568.
- Fan, J.-Y., Tercel, M. & Denny, W. A. (1997). Anti-Cancer Drug Des.12, 277–293. [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Karolak-Wojciechowska, J., Mrozek, A., Amiel, P., Brouant, P. & Barbe, J. (1996). Acta Cryst. C52, 2939–2941.
- Neidle, S. (1979). Prog. Med. Chem.16, 151–221. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Prasad Krishna, B. N., Banasal, I., Das, P. & Srivastava, R. (1984). Curr. Sci.53, 778–780.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Talacki, R., Carrell, H. L. & Glusker, J. P. (1974). Acta Cryst. B30, 1044–1047.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903267X/bt5021sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903267X/bt5021Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report