Figure 4.
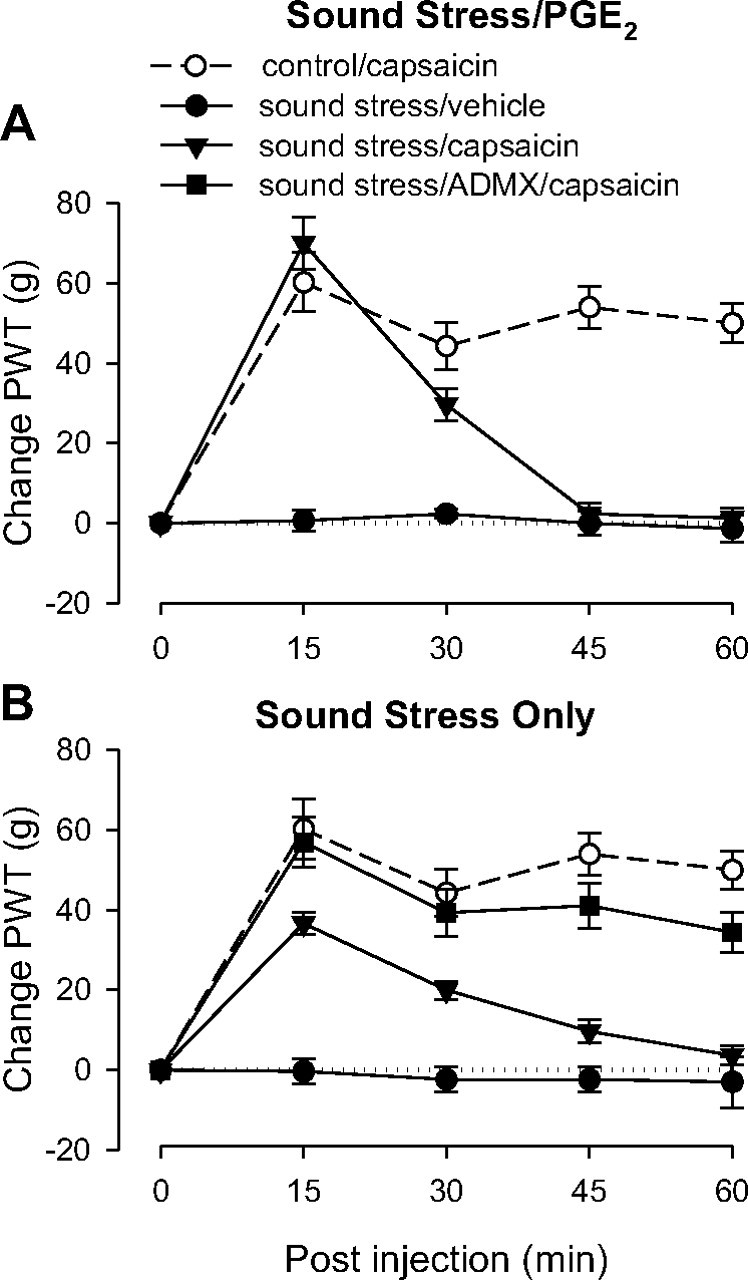
Effect of chronic widespread pain on capsaicin-induced analgesia. All groups of rats except controls experienced chronic unpredictable sound stress (see Materials and Methods) 14 d before testing. On the day of testing, 2.5 h before the experiment stressed rats received intradermal injections of either PGE2 or its vehicle on the dorsum of the hindpaw. A, PGE2. As expected, the pre-capsaicin baseline for both groups that received PGE2 was lower than the control group (data not shown). Paw-withdrawal thresholds (PWT) remained low for the group that received capsaicin vehicle, but the group that received capsaicin showed early antinociception that lasted only to the 30 min time point, indicating antagonism of capsaicin-induced analgesia duration; n = 6 for both sound stress groups. Data from control group are replotted from Figure 1 for comparison. B, No PGE2 pretreatment. Adrenal-intact rats showed short duration analgesia with a time course similar to that of the rats who received PGE2 (A), indicating that antagonism of capsaicin-induced analgesia was not due to PGE2 administration. This effect was abolished in ADMX rats, suggesting that the shortened analgesic duration is mediated by the sympathoadrenal axis.
