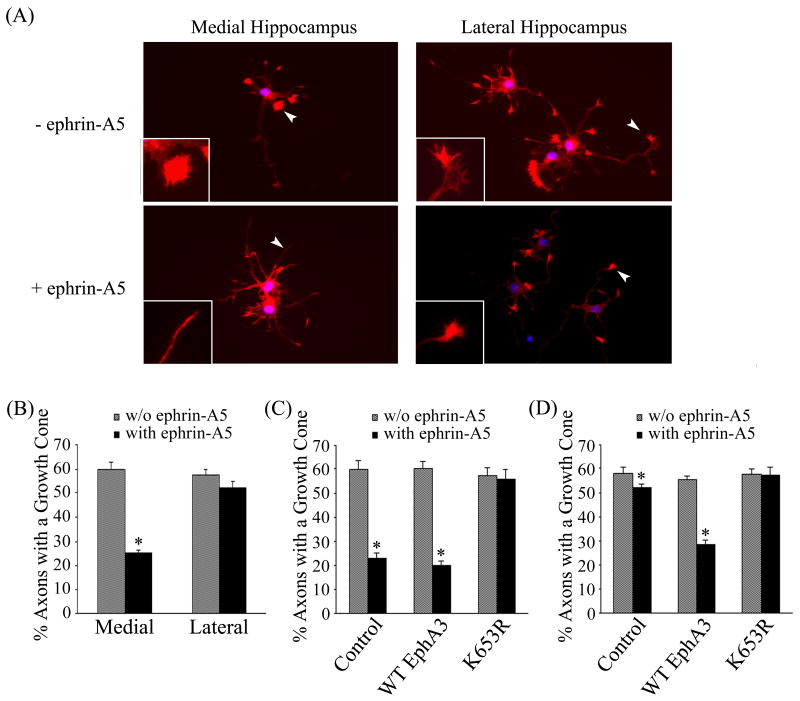
Figure 6. Medial and lateral hippocampal neurons response to ephrin-A5 treatment differently.
(A) Hippocampal neurons from rat E17 embryos were culture in neurobasal media for 48 hours. The cultures were treated with 2 μg/ml clustered ephrin-A5 for 15 minutes and stained for F-actin with Texas Red® conjugated phalloidin. The growth cone morphology was examined under a Zeiss fluorescence microscope. Arrowheads indicate representative growth cones shown in inserts. (B) Ephrin-A5 induces significant growth cone collapse in medial but not lateral hippocampal neurons. The number of the total axons and axons with a growth cone were enumerated, expressed as the percentage of axons that contain growth cones. Bars represent the means of at least 300 axons from three independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviation. Asterisk * indicates α < 0.05 vs culture without ephrin-A5 treatment (one-way ANOVA followed with Bonferroni test for selected pairs). (C) Medial hippocampal neurons were transfected with wild type or kinase-dead EphA3 plus GFP and treated with or without ephrin-A5. Growth collapse was quantified as in (B). Only green cells were counted. (D) Lateral hippocampal neurons were transfected with wild type or kinase-dead EphA3 plus GFP and treated with or without ephrin-A5. Growth collapse was quantified as in (B). Only green cells were counted.