Figure 2.
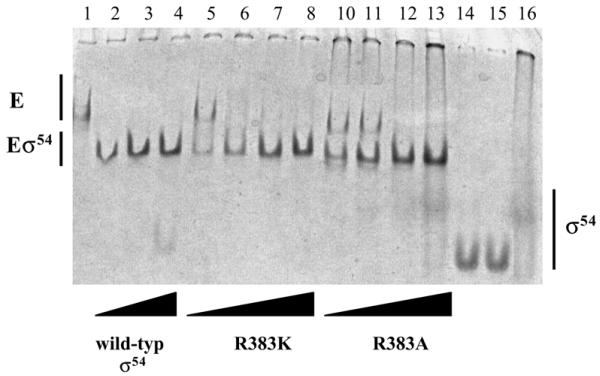
Binding of σ54 to E.coli core RNAP. Native gel holoenzyme assembly assays were used to detect complexes forming between core RNAP and R383K and R383A, respectively. The formation of holoenzyme (Eσ54) was detected as the presence of a faster migrating species when compared with core (E, lane 1) alone. Titrations of core RNAP with σ54 were carried out using 250 nM core RNAP and increasing concentrations of σ54 at ratios of 1:1 (lanes 2, 5 and 10), 1:2 (lanes 3, 6 and 11), 1:4 (lanes 4, 7 and 12) and 1:8 (lanes 8 and 13). Wild-type σ54 shifted nearly all the core into the holoenzyme form at a 1:1 molar ratio of core to σ54 (lane 2); in contrast, R383K shifted all the core to the holoenzyme form at a ratio of 1:2 (lane 6) and R383A at 1:4 (lane 12). Free σ54 (2.5 µM) proteins are also shown: lane 14, wild-type; lane 15, R383K; lane 16, R383A.
