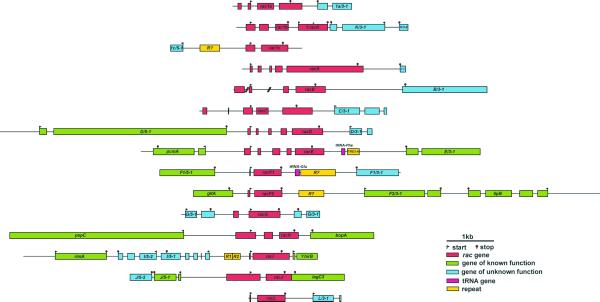
Figure 1.
Genomic structure of the Dictyostelium rac family. 73.1 kb genomic DNA has been assembled in 15 contigs. Contigs are aligned at the start codon of rac genes. Bars indicate coding sequences and are extended beyond the start and stop codon to indicate untranslated but transcribed sequences, when supported by EST clones. Genes other than rac genes have been named according to their position relative to the rac gene of the corresponding contig (see Table S1 in Supplementary Material for a description). Lines indicate intergenic and intron sequences. When more than one termination site was identified, the most distant has been depicted. A frameshift caused by a 5 nt deletion in ΨracK is indicated by #. Two introns of racB are not covered by genomic clones (indicated by slashes). Less than half of the protein ORFs identified correspond to genes whose function is known in Dictyostelium or in other species. Accession numbers for the contigs: rac1a, AF309947; rac1b, AF310884; rac1c, AF310885; racA, AF310886; racB, AF310887; racC, AF310888; racD, AF310889; racE, AF310890; racF1, AF037042; racF2, AF310892; racG, AF310893; racH, AF310894; racI, AF310895; racJ, AF310896; racL, AF310897. The contig for racE extends sequence U41222. The contig for racH overlaps with sequence AF104350, which lacks the racH gene. The contig for racF2 overlaps with sequence AF019108.