Figure 3.
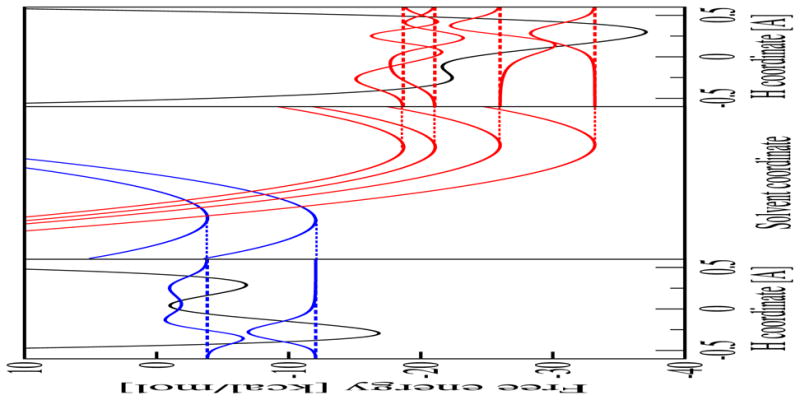
Analysis of the free energy surfaces for the PCET reaction in the phosphate-acceptor model for the rhenium-tyrosine complex. In the center frame are slices of the two-dimensional ET diabatic free energy surfaces as functions of the solvent coordinates. The slices were obtained along the line connecting the minima of the lowest energy reactant (I) and product (II) two-dimensional free energy surfaces. In the left frame is the reactant (I) proton potential energy curve and the corresponding proton vibrational wavefunction as a function of the proton coordinate evaluated at the minimum of the ground state reactant free energy surface. In the right frame is the product (II) proton potential energy curve and the corresponding proton vibrational wavefunction as a function of the proton coordinate evaluated at the minimum of the ground state product free energy surface. Figure reproduced with permission from Ref. [37].
