Fig. 3.
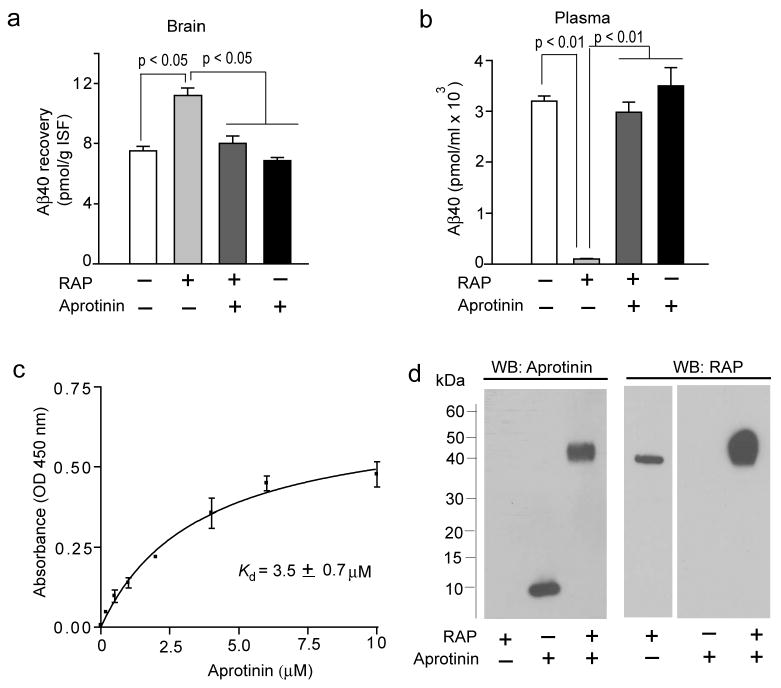
Levels of human Aβ40 in the brain (a) and plasma (b) 30 min after microinjection of human Aβ40 (40 nM) and 14C-inulin (0.023 μCi) into the mouse caudate nucleus in the presence and absence of RAP (5 μM) with and without aprotinin (8.6 μM). Human unlabeled Aβ40 peptide levels in the brain and plasma were determined by using human-specific ELISA, as described (Bell et. al. 2007). The brain sample used for analysis was approximately 15 mg of tissue adjacent to the site of microinjection in the caudate nucleus as described (Bell et al. 2007). In (a) and (b), values are mean ± SEM from 3 to 5 independent experiments. (c) Binding of aprotinin to immobilized human RAP, by ELISA. Briefly, 5 μg/mL repurified human recombinant RAP (Oxford Biomedical Research, Oxford, MI, USA) was coated on microtiter plate and wells were blocked with 1% BSA. Varying concentrations of aprotinin (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA) were added to the wells and incubated for 1 h at 25°C. Bound aprotinin was detected by mouse anti-aprotinin antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), followed by goat anti-mouse HRP conjugate (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The reaction was developed using tetramethyl benzidine substrate (TMB; KPL), stopped with 1M HCl and quantified at 450 nm. Values are mean ± s.e.m. from 3 independent experiments. (d) Formation of RAP and aprotinin complexes detected by the Western blot analysis for aprotonin and RAP. Aprotinin (2 μM; Sigma) was incubated with human recombinant RAP (2 μM; Oxford Biomedical Research) for 1 h at 37°C in PBS and the complex formation was confirmed by cross-linking with Bis(sulfosuccinimidyl)suberate (BS3; Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) followed by 4-12% SDS-PAGE separation of proteins under non-reducing conditions and Western blot analysis for aprotinin using mouse anti-aprotinin (Abcam) antibody and for RAP using mouse anti-RAP (Oxford Biomedical Research). Representative WB analysis from 3 independent experiments were shown.
