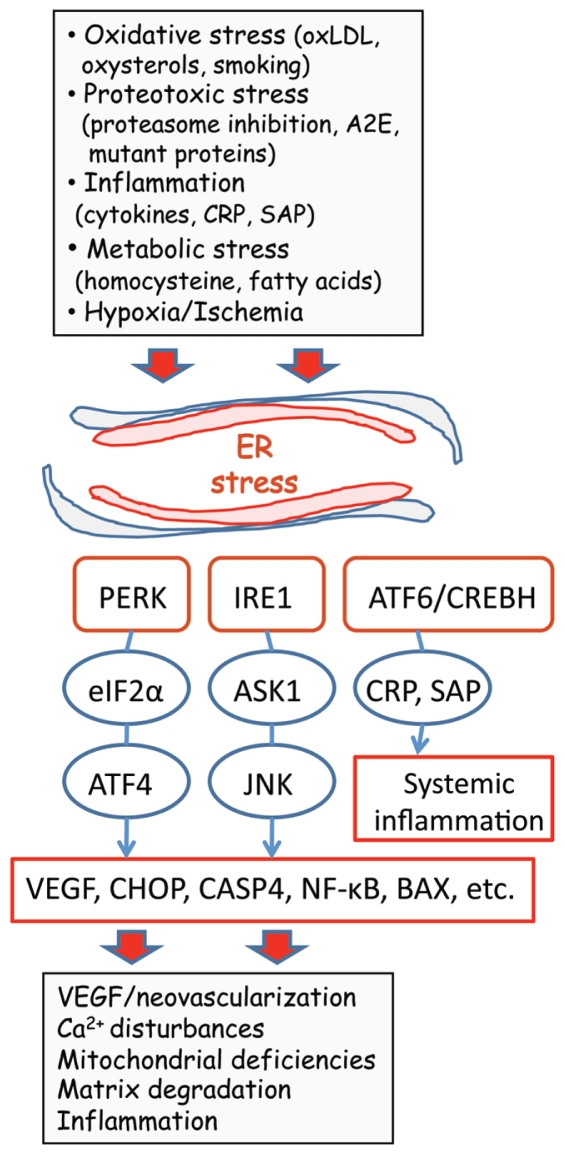
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation depicting the role of ER stress in the pathogenesis of neovascular AMD. Several AMD risk factors trigger ER stress and activate UPR signaling via IRE1, PERK and ATF6/CREBH transducers. UPR induces the expression of stress resistance components, but excessive and prolonged insults can trigger the expression of VEGF, CHOP, CASP4 and NF-κB, evoking neovascularization and pathological changes in the macula region. Only the pathways known to be present in human RPE cells have been included.