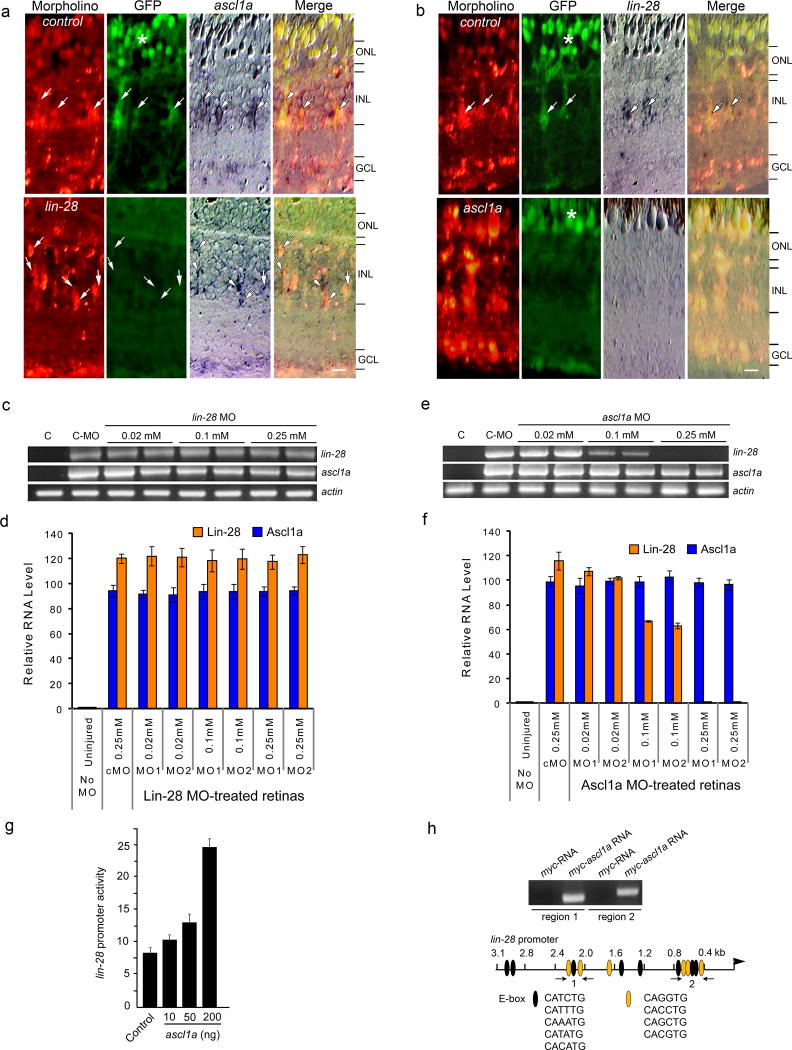
Figure 3.
Ascl1a regulates lin-28 expression. (a, b) Lissamine-labeled control, ascl1a or lin-28-targeting MOs were electroporated into injured retinas of 1016 tuba1a:gfp transgenic zebrafish. At 4 dpi GFP, and ascl1a and lin-28 mRNA expression was detected by immunofluorescence and in situ hybridization, respectively. Control MO-treated retinas retain GFP, ascl1a and lin-28 expression (arrows), while Lin-28 knockdown suppresses GFP expression and knockdown of Ascl1a suppresses both GFP and lin-28 expression. Scale bar is 10 microns. (c,d) RT-PCR shows Lin-28 knockdown has no effect on injury-dependent induction of ascl1a mRNA at 2 dpi (c), while Ascl1a knockdown blocks injury-dependent induction of lin-28 mRNA at 2 dpi (d). Lane C is control uninjured retina. (e,f) Real-time PCR quantification of the effects of Lin-28 (e) or Ascl1a (f) knockdown on lin-28 and ascl1a mRNA levels at 2 dpi. Data are normalized to uninjured retinas and represent means ± s.d. from 3 replicas of a single experiment. (g) Ascl1a regulates lin-28 promoter activity. HEK293 cells were transfected with lin-28:luciferase and the indicated amounts of cmv:ascl1a along with SV40:Renilla luciferase for normalization. Normalized promoter activity is reported as means ± s.d. (n=3; compared to control, P=0.0123 for 50 ng Ascl1a expression vector and P=0.0001 for 200 ng of Ascl1a expression vector). (h) Ascl1a binds to regions of the lin-28 promoter that harbor multiple E-boxes. ChIP analysis of zebrafish embryos (single cell stage) injected with either myc-RNA or myc-ascl1a mRNA. Immunoprecipitated chromatin was assayed by PCR using primers (arrows) flanking putative Ascl1a binding sites 1 and 2 (ethidium bromide stained gel shown). The predicted fragments sizes of 287 bp and 323 bp were amplified. The 3.1 kb lin-28 promoter diagramed below the gel shows consensus E-box binding sites (ovals). Orange ovals are putative Ascl1 binding sites.