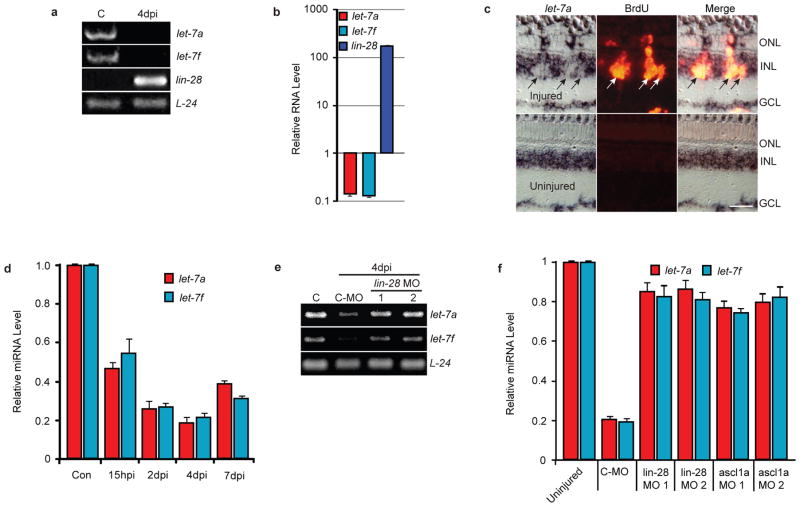
Figure 4.
Lin-28 regulates let-7 miRNA levels in MG-derived progenitors. (a) RT-PCR shows let-7 miRNA expression is high and lin-28 expression is low in differentiated MG (lane C), while let-7 miRNA expression is suppressed and lin-28 expression is highly induced in MG-derived progenitors at 4 dpi. (b) Real-time PCR quantification of lin-28 mRNA and TaqMan PCR quantification of let-7a and let-7f miRNA levels in purified MG and MG-derived progenitors at 4 dpi. Data are normalized to uninjured retina and represent means ± s.d. A single sample, consisting of MG purified from 2 uninjured fish and MG-derived progenitors purified from 10 injured fish, was assayed in triplicate. (c) let-7a in situ hybridization (LNA probe) and BrdU immunofluorescence shows a dearth of let-7a miRNA in BrdU+ MG-derived progenitors of the injured retina at 4dpi. Scale bar is 20 microns. (d) TaqMan PCR quantification of let-7 miRNA levels in uninjured and injured retinas at different times after injury. Data represent means ± s.d. (n=3 fish; compared to control uninjured retina, P=0.0001 or less for let-7a and let-7f at all time points). (e) RT-PCR shows Lin-28 knockdown with 2 different MOs relieves injury-dependent let-7a and let-7f miRNA suppression. Lane C is uninjured retina. (f) Lin-28 or Ascl1a knockdown relieves injury-dependent let-7 miRNA suppression. TaqMan PCR was used to quantify let-7a and let-7f miRNA levels. Data represent means ± s.d. from 3 replicas of a single experiment.