Figure 1.
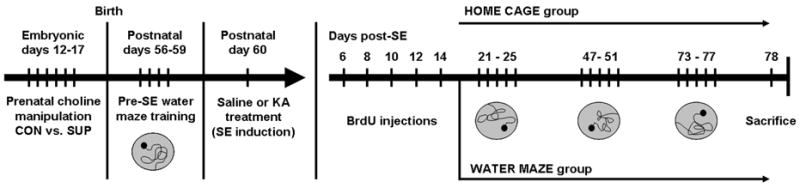
Timeline of experimental procedures. Adult rat offspring from dams that received either a choline control (CON) or supplemented (SUP) diet during embryonic days 12–17 were all trained in the water maze at postnatal day (P) 56 for 4 days. On P60, CON and SUP rats were given injections of saline or kainic acid (KA) to induce status epilepticus (SE). All rats were then given an injection of BrdU on days 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14 after SE. Saline- and KA-treated CON and SUP rats then either remained in their home cage, or were given three additional water maze testing sessions at 3, 6.5, and 10 weeks after SE, each session lasting 5 days. All rats were then sacrificed one day after the last water maze testing session at approximately 11 weeks after SE.
