Figure 5.
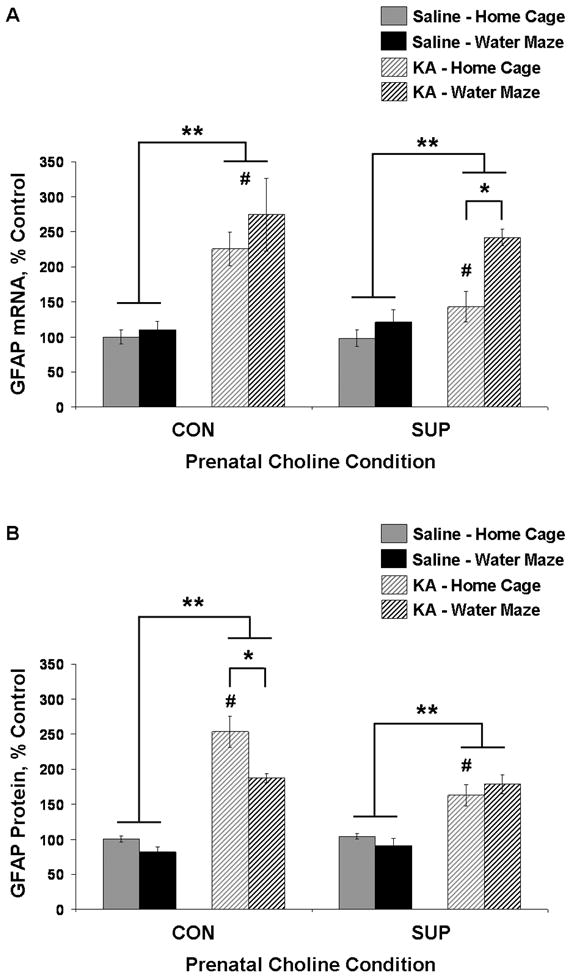
Mean (± SEM) percent of control levels for hippocampal GFAP mRNA (A) and protein (B) for CON and SUP rats that were treated with saline (solid bars) or KA (hatched bars) and that remained in their home cage (grey) or received additional water maze training (black) following treatment. Both CON and SUP rats showed a significant overall SE-induced increase in GFAP mRNA and protein expression, but this increase was attenuated in KA-treated home cage SUP rats. Repeated water maze training attenuated elevated GFAP protein levels in KA-treated CON rats, and further increased GFAP mRNA levels in KA-treated SUP rats. * significantly different at p < 0.05; ** main effect of seizure revealed by a within diet 2-way ANOVA (seizure × experience), p < 0.05; # KA-treated home cage SUP rats are significantly different from KA-treated home cage CON rats (A, B) and KA-treated water maze CON rats (A).
