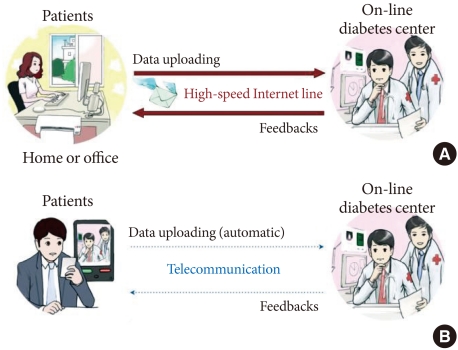
Fig. 1.
(A) A scheme of the Internet-based glucose monitoring system. Patients logged on to the website from their homes or offices at a time and uploaded their glucose data, together with additional information such as current drug information (the type and dosage of oral hypoglycaemic medications or insulin), lifestyle modifications and hypoglycaemic events. In addition, patients recorded any changes in their blood pressure or weight, and any questions or detailed information that they wished to discuss, such as changes in diet, exercise, hypoglycaemic events, and other factors that might influence their blood glucose level. Medical team of on-line diabetes center reviewed the uploaded information and sent optimal feedbacks to the patients periodically. (B) A scheme of the telecommunication based glucose control system in which mobile devices such as a mobile phone with the capacity to measure blood glucose were adopted. Patients could upload their self-monitoring of blood glucose data through telecommunication automatically and the medical team responded to patients after reviewing the uploaded data. The patient-doctor communication could be achieved practically in real time by the short message service.