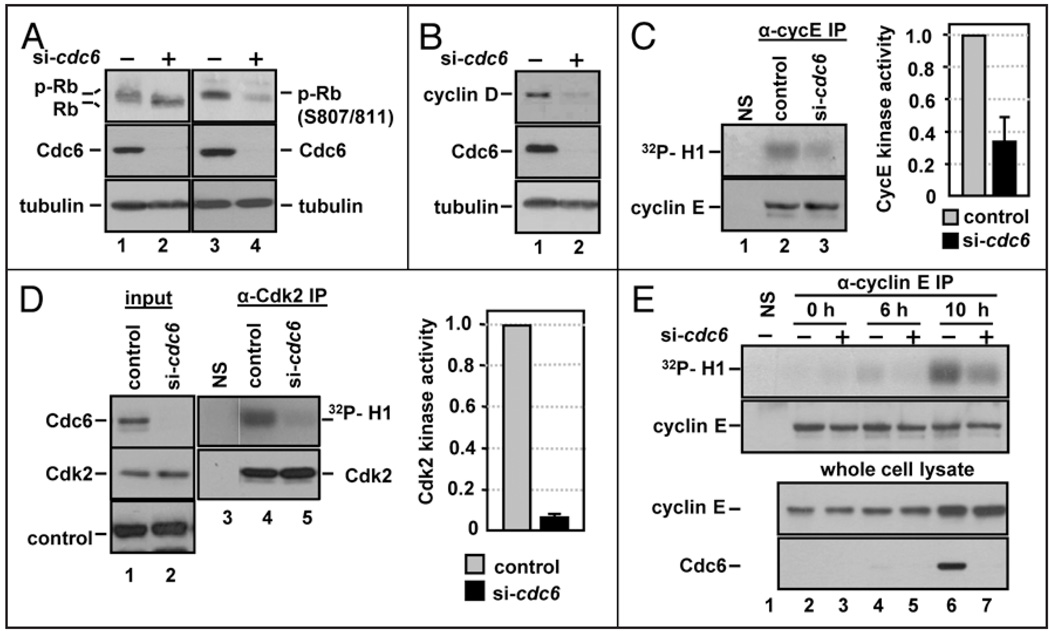
Figure 2.
Cdc6 depletion prevents cyclin E/Cdk2 activation during G1. (A) Whole cell extracts from NHF1 cells transfected with control or cdc6 siRNA as in Figure 1D were probed with antibodies to total Rb or with a phosphospecific antibody that recognizes Rb phosphorylated at S807 and S811 and for total Cdc6 and tubulin. (B) Whole cell extracts from siRNA-transfected NHF1 were probed with antibodies to cyclin D1, Cdc6 and tubulin. (C) Extracts of siRNA-transfected NHF1 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with normal rabbit serum (“NS” lane 1) or with anti-cyclin E antibody (lanes 2 and 3). The precipitates were divided and analyzed by immunecomplex kinase assay with purified histone H1 and [γ-32P]ATP, followed by SDS-PAGE (top row) or analyzed for cyclin E protein by immunoblotting (bottom row). The bar graph reports average cyclin E-associated H1-kinase activity in cells depleted of Cdc6 relative to the corresponding control cells in three independent experiments. (D) Extracts of siRNA-transfected NHF1 cells were treated as in (C), except that the immunoprecipitations and immunoblot utilized anti-Cdk2 antibody. The bar graph reports average Cdk2 H1-kinase activity in cells depleted of Cdc6 relative to the corresponding control cells in three independent experiments. (E) NHF1 cells were transfected with a total of 100 nM of control or cdc6 siRNA for 12 h, then incubated for 72 h in medium containing low serum (0.1% FBS). Cells were released from growth arrest by addition of 10% FBS, labeled for 1 h with BrdU immediately prior to each collection point at 0, 6 and 10 hours after serum addition. Immunecomplex kinases assays were performed as in (C).