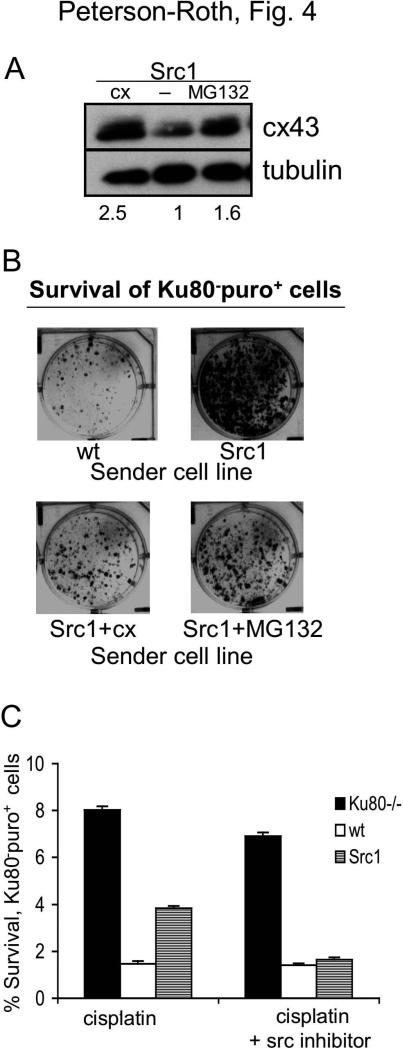
Figure 4. Inhibition of v-Src kinase activity or overexpression of connexin overcomes the increased survival conferred on neighboring cells by v-Src.
(A) Western blot analysis of cx43 expression in Src1 cells, Src1 cells transfected with a vector expressing human cx43 cDNA, or Src1 cells treated with the proteasome inhibitor, MG132 (100nM for 24 h). Value below each lane represent levels of cx43 expression in each sample relative to untreated Src1 cells (normalized to tubulin). (B) Visualization of monolayer growth (in the presence of puro) by Ku80-puro+ receiver cells co-mixed with the indicated MEF-derived cell lines: WT MEFs; MEFs expressing v-Src (Src1); Src1 cells overexpressing cx43 by gene transfer (Src1+cx); and Src1 cells pre-treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132. Puro selection restricted growth only to the Ku80-puro+ receiver cells. (C) Clonogenic survival of Ku80-puro+ receiver cells co-mixed with the indicated sender cell line and treated with cisplatin in the presence or absence of the Src tyrosine kinase inhibitor PP2, as indicated. Mixed cell populations were seeded at high density, treated with PP2, then exposed to cisplatin. Following treatment, cisplatin and PP2 were removed, cells were washed with PBS, trypsinized and reseeded at low density in the presence of puro to specifically detect growth of Ku80-puro+ receiver cell colonies.