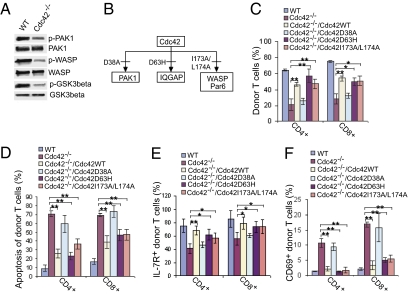
Fig. 5.
The Cdc42 mutant defective in binding to PAK1 cannot rescue T-cell homeostasis. (A) Cdc42 deficiency causes an impaired activation of Cdc42 effectors. Pan T cells were purified from splenocytes of WT and Cdc42−/− mice and Western blotted with antibodies against phosphorylated (p) and total PAK1, WASP, and GSK3β. (B) Cdc42 mutants cannot bind to certain effectors. Cdc42D38A is defective in binding to PAK1, Cdc42D63H is defective in binding to IQGAP, and Cdc42I173AL174A is defective in binding to WASP and Par6. (C–F) Reconstitution of Cdc42D38A into Cdc42−/− T cells cannot rescue T-cell homeostasis. Bone marrow cells from WT and Cdc42-deficient mice were transduced with the indicated constructs. The transduced bone marrow cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated BoyJ mice. Recipient mice were killed 2 mo later. Splenocytes were prepared and analyzed for frequency (C), apoptosis (D), IL-7R expression (E), and activation status (F) of CD45.2+ donor naive T cells. Data are shown as means ± SD; n = 4. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05.