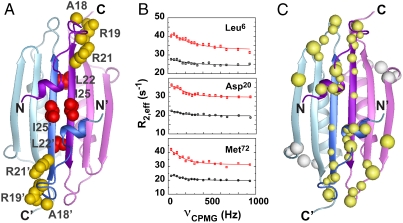
Fig. 4.
(A) Residues important for stimulation of MinD-catalyzed hydrolysis are either partly solvent accessible (yellow side chains) or completely inaccessible (red) in the dimeric structure of full-length Ng-MinE. (B) Representative relaxation dispersion curves for backbone amide groups at 800 MHz (red) and 500 MHz (black) shown for the three residues indicated. (C) Backbone amides undergoing statistically significant exchange (> 99% confidence by F test) are shown as balls, where the diameter is linearly scaled according to the measured exchange rate (300 s-1–3100 s-1). Most exchange sites cluster to a contiguous region on each end of the dimer (yellow). A structurally distinct site of exchange was also detected for αC (white). No exchange was detected for amides in the αB helices.