Abstract
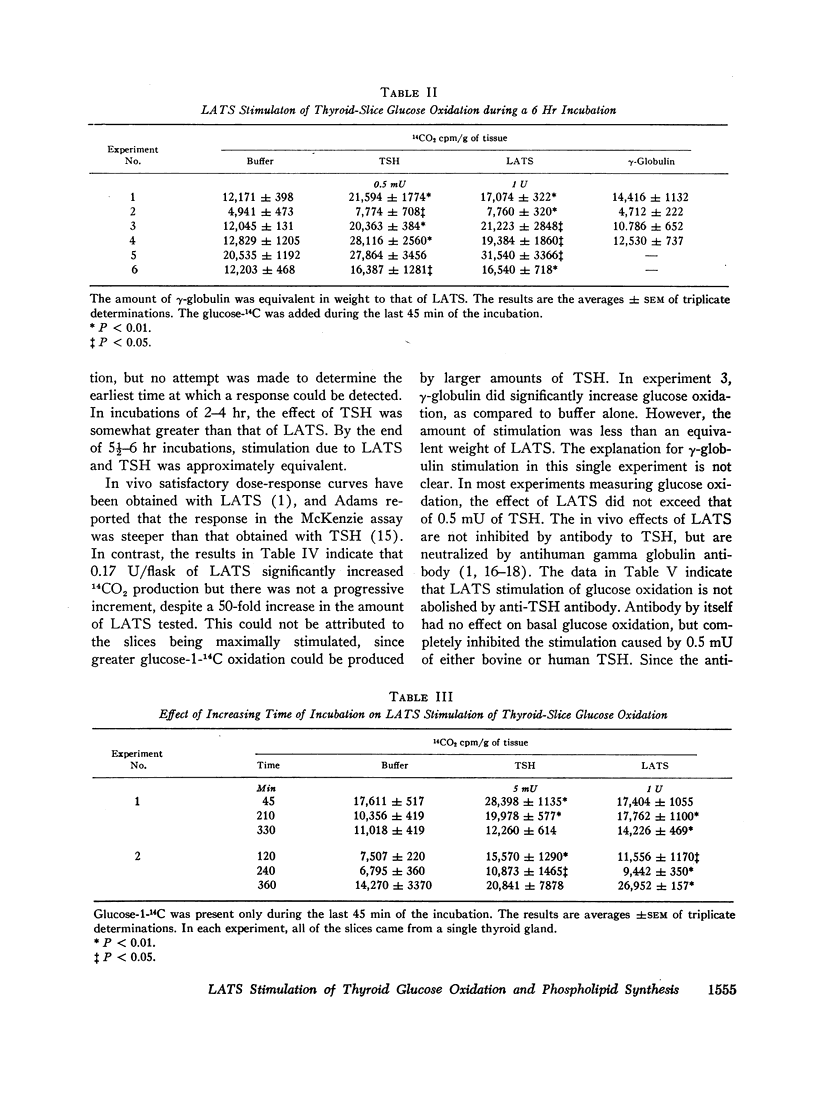
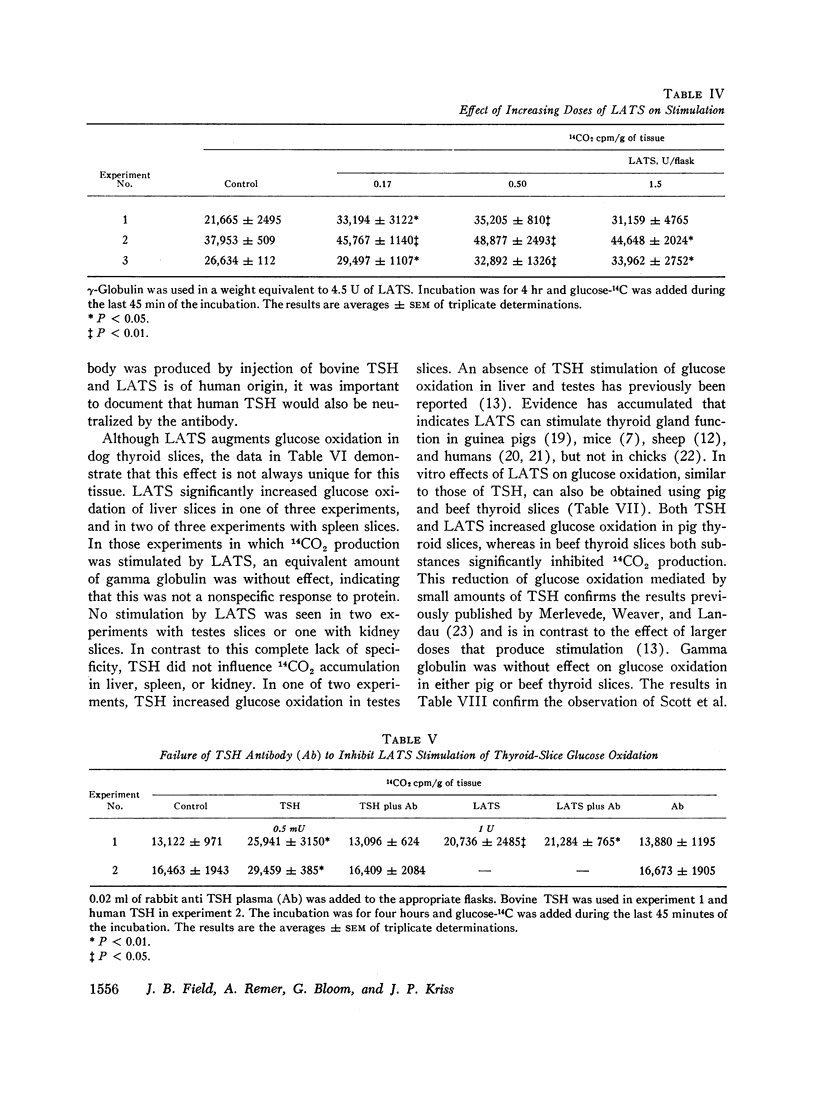
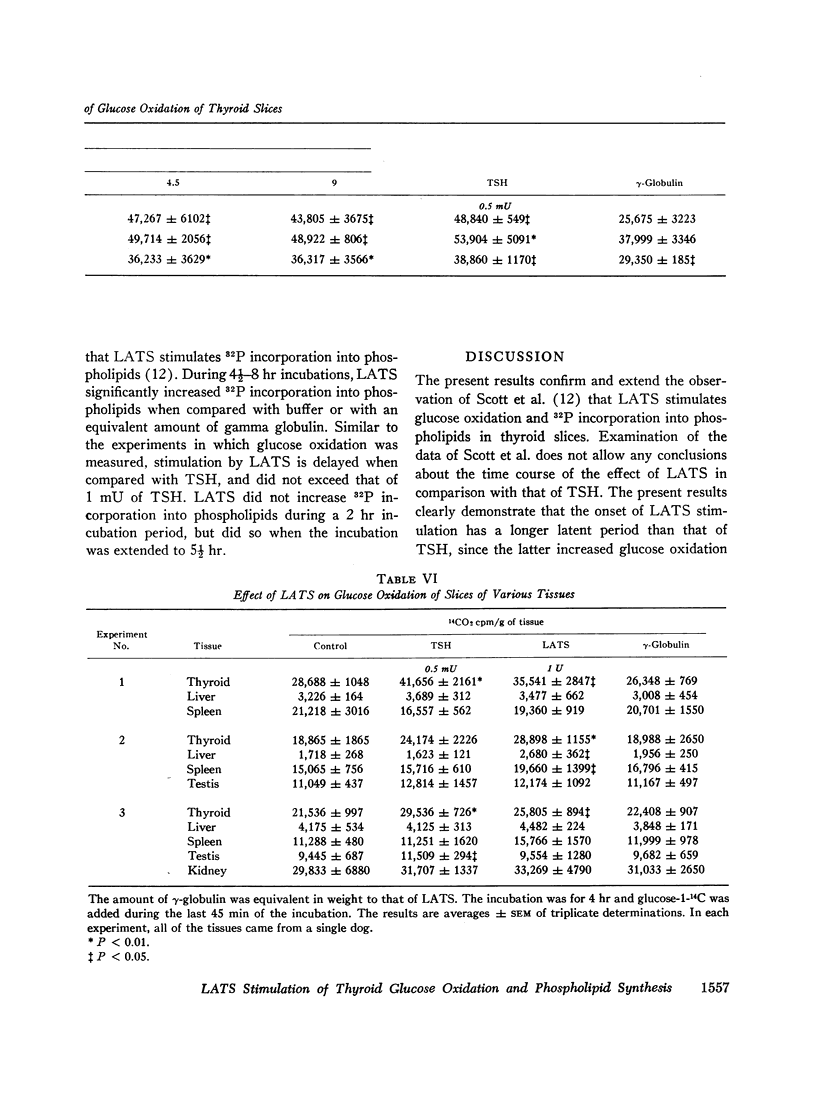
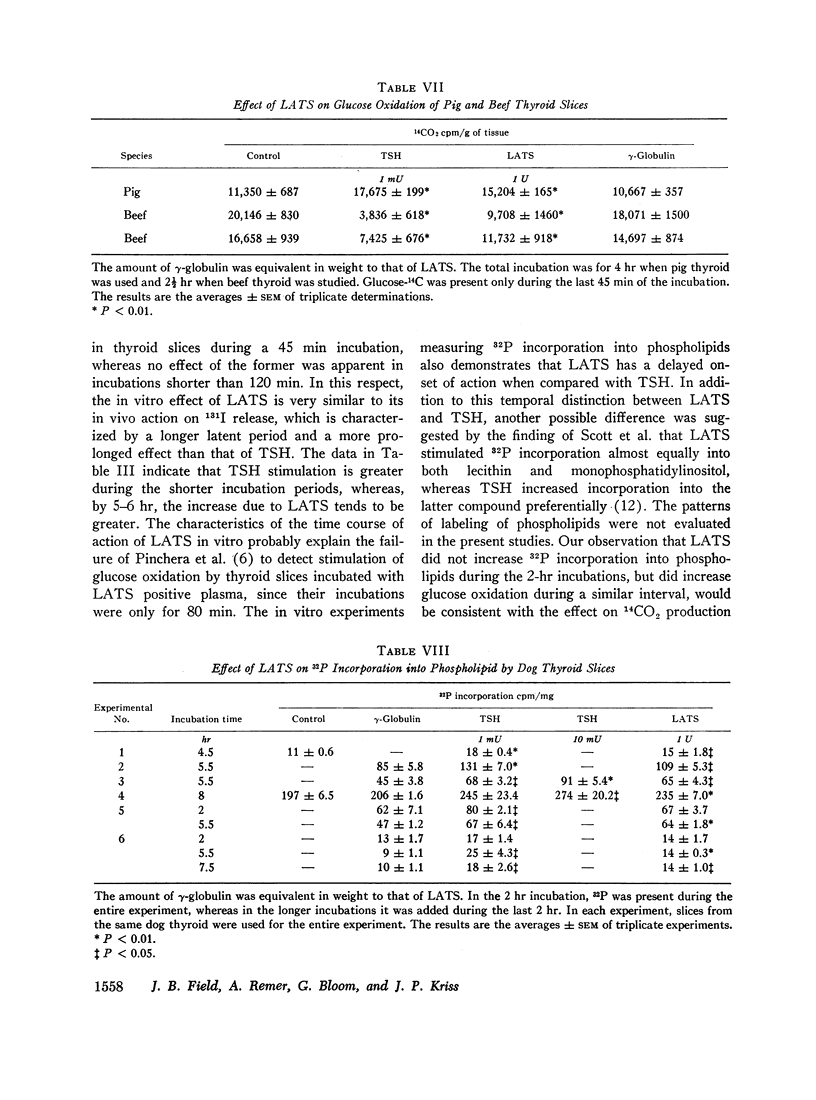
Long-acting thyroid stimulator (LATS) increased glucose oxidation and 32P incorporation into phospholipids in in vitro experiments with dog thyroid slices. The time course of the response was different from that obtained with thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), but was very similar to the delayed effect observed in vivo. During a 45 min incubation, TSH, but not LATS increased glucose oxidation, whereas in longer experiments up to 6 hr, both substances augmented 14CO2 production. Amounts of pooled human gamma globulin equivalent to LATS were inactive. Although TSH stimulated 32P incorporation into phospholipids during a 2 hr incubation, LATS was ineffective. In longer incubations, from 4½ to 8 hr, LATS did increase 32P incorporation. The stimulatory effect of LATS was not abolished by anti-TSH antibody capable of neutralizing human TSH. Effects of LATS were also obtained with beef and pig thyroid slices. In addition to stimulation of glucose oxidation in dog thyroid slices, LATS occasionally also stimulated glucose oxidation in dog spleen and liver slices. Despite a 54-fold increase in LATS concentration, a satisfactory dose-response curve could not be demonstrated when 14CO2 production was measured.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS D. D. Bioassay of long-acting thyroid stimulator (L.A.T.S.); the dose-response relationship. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Jul;21:799–805. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-7-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADAMS D. D. PATHOGENESIS OF THE HYPERTHYROIDISM OF GRAVES'S DISEASE. Br Med J. 1965 Apr 17;1(5441):1015–1019. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5441.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADAMS D. D. The presence of an abnormal thyroid-stimulating hormone in the serum of some thyrotoxic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Jul;18(7):699–712. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-7-699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARNAUD C. D., KNEUBUHLER H. A., SEILING V. L., WIGHTMAN B. K., ENGBRING N. H. RESPONSES OF THE NORMAL HUMAN TO INFUSIONS OF PLASMA FROM PATIENTS WITH GRAVES' DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44:1287–1294. doi: 10.1172/JCI105235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BJORKMAN S. E., DENNEBERG T., HEDENSKOG I. Clinical evaluation of the thyroid stimulating hormone activity in exophthalmos. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1961 Dec;38:577–584. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0380577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall G. N., Solomon D. H. Inhibition of long-acting thyroid stimulator by thyroid particulate fractions. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):552–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI105369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berumen F. O., Lobsenz I. L., Utiger R. D. Neutralization of the long-acting thyroid stimulator by thyroid subcellular fractions. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):640–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro L., Dorrington K. J., Munro D. S. Relation between long-acting thyroid stimulator and thyroid function in thyrotoxicosis. Lancet. 1966 Oct 22;2(7469):878–880. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91978-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD J. B., PASTAN I., JOHNSON P., HERRING B. Stimulation in vitro of pathways of glucose oxidation in thyroid by thyroid-stimulating hormone. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:1863–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISS J. P., PLESHAKOV V., CHIEN J. R. ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE LONG-ACTING THYROID STIMULATOR AND ITS RELATION TO HYPERTHYROIDISM AND CIRCUMSCRIBED PRETIBIAL MYXEDEMA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1005–1028. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepp A., Oliner L. Failure of long-acting thyroid stimulator globulin (LATS) and serum to stimulate thyroid function in the chick. Endocrinology. 1967 Feb;80(2):369–374. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKENZIE J. M., FISHMAN J. Effects of antiserum in bioassay of thyrotropin and thyroid activator of hyperthyroidism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:126–128. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKENZIE J. M. REVIEW: PATHOGENESIS OF GRAVES' DISEASE: ROLE OF THE LONG-ACTING THYROID STIMULATOR. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Mar;25:424–461. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-3-424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEEK J. C., JONES A. E., LEWIS U. J., VANDERLAAN W. P. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE LONG-ACTING THYROID STIMULATOR OF GRAVES' DISEASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:342–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERLEVEDE W., WEAVER G., LANDAU B. R. Effects of thyrotropic hormone on carbohydrate metabolism in thyroid slices. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1160–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI104801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M. The long-acting thyroid stimulator: its role in Graves' disease. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:1–46. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOGUCHI A., KURIHARA H., SATO S. CLINICAL STUDIES ON THE LONG-ACTING THYROID STIMULATOR. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Feb;24:160–165. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-2-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka H., Field J. B. Effects of ions on TSH stimulation of P-32 incorporation into thyroid slice phospholipid. Am J Physiol. 1966 Dec;211(6):1357–1360. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.6.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINCHERA A., PINCHERA M. G., STANBURY J. B. THYROTROPIN AND LONG-ACTING THYROID STIMULATOR ASSAYS IN THYROID DISEASE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Feb;25:189–208. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-2-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Katzen R. Activation of adenyl cyclase in thyroid homogenates by thyroid-stimulating hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Dec 29;29(6):792–798. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. The effect of dibutyryl cyclic 3',5'-AMP on the thyroid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 5;25(1):14–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90632-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. W., Good B. F., Ferguson K. A. Comparative effects of long-acting thyroid stimulator and pituitary thyrotropin on the intermediate metabolism of thyroid tissue in vitro. Endocrinology. 1966 Nov;79(5):949–954. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-5-949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishiba Y., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Comparison of early effects of thyrotropin and long-acting thyroid stimulator on thyroid secretion. Endocrinology. 1967 May;80(5):957–961. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-5-957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


