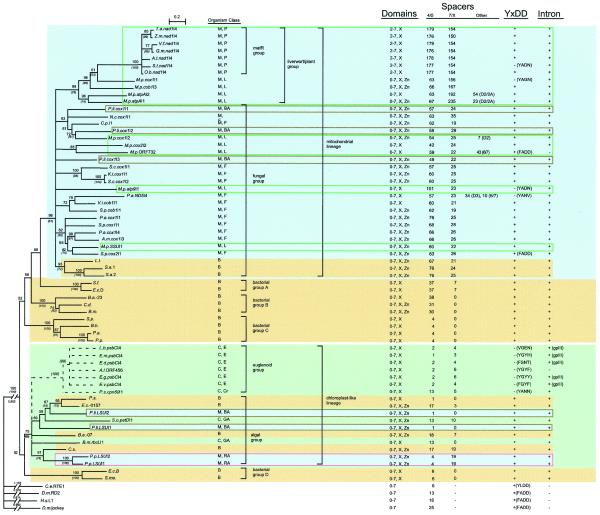
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic model of group II intron ORF relationships. The phylogenetic estimate was based on RT subdomains 0–7 and domain X, and was calculated by a neighbor-joining algorithm (PHYLIP; see Materials and Methods). The tree was rooted with four RTs of non-LTR retroelements: Caenorhabditis elegans RTE1 (accession number AF025462), Drosophila melanogaster RD2 (X51967), Homo sapiens L1 (U93574) and D.melanogaster jockey (M22874) (8). Bootstrap values are expressed as percentages, and were derived from 1000 (NJ) or 100 (MP) samplings, with MP values shown in italics and parentheses. Nodes with <50% support are collapsed. The predicted approximate location of euglenoid ORFs is shown with dotted lines (see text). Juxtaposed with the inferred phylogenetic relationships are properties of the introns, including protein domains present (subdomains 0–7 of the RT domain, domain X, Zn domain), the size of spacer segments between conserved motifs (see Fig. 2 for spacer definitions), idiosyncratic insertions, the presence of the YADD motif or a functional substitute (see Table 3 footnote), and the presence of a group II intron structure (see Table 3). Euglenoid ORFs are found in group III introns; P.s.cpn60I1 is reported to be a twintron (46), but the published RNA structure is probably incorrect. Abbreviations and color codings are: M (mitochondria; blue), C (chloroplast; green), B (bacteria; yellow), P (higher plant; green outline), L (liverwort; green outline), F (fungus; no outline), BA (brown alga; brown outline), GA (green alga; no outline), RA (red alga; pink outline), E (euglenoid; no outline), Cr (cryptopmonad; no outline).