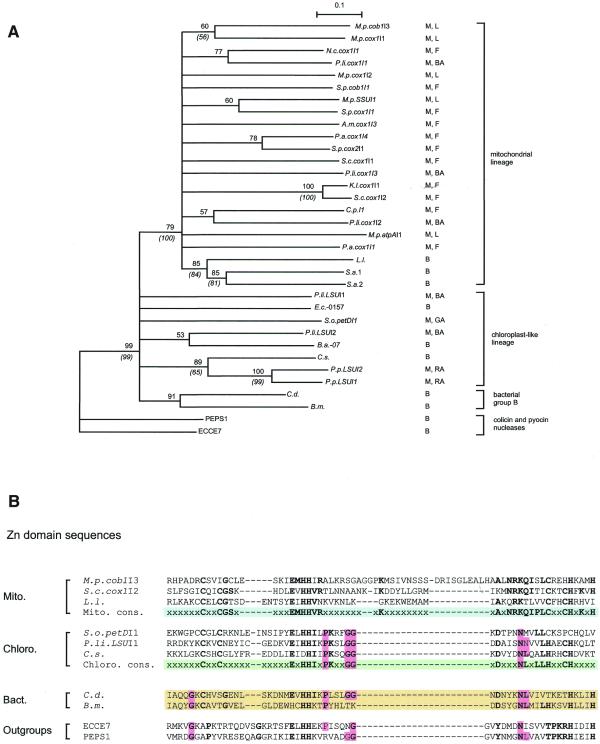
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of the Zn domain. (A) A phylogenetic tree of the Zn domain was derived by neighbor-joining analysis with 1000 bootstrap samplings, or by maximum parsimony with 100 bootstrap samplings (italics and parentheses). The tree was rooted with nuclease domains of E.coli colicin E7 (ECCE7; accession number 144375) and P.aeruginosa pyocin S1 (PEPS1; accession number Q06583). (B) Alignment of the Zn domains of selected group II intron ORFs and the nuclease domains of ECCE7 PEPS1. A 50% consensus sequence is shown for chloroplast-like and mitochondrial lineages. x represents residues with <50% conservation. Positions marked in bold show group-specific consensus sequences (mitochondrial, chloroplast-like and colicin/pyocin), or show agreement with the consensus sequence of another group (C.d. and B.m.). Pink shading indicates similarities between colicin/pyocin nuclease domain and bacterial or chloroplast-like Zn domains. The consensus sequence for the colicin/pyocin family of nucleases is a 100% consensus sequence according to Gorbalenya (9).