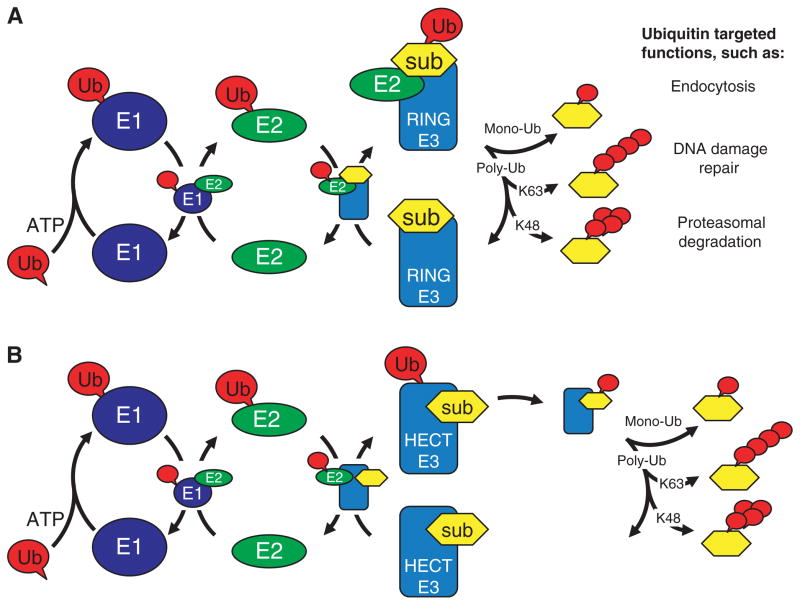
Fig. 1.
The ubiquitination pathway. Diagram illustrating protein–protein interactions that mediate the E3 dependent ubiquitination of substrates. (A) The pathway utilized by RING and U-box E3s and (B) the pathway utilized by HECT domain E3s. Proteins are noted as Ub (ubiquitin), E1 (ubiquitin-activating enzyme), E2 (ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme), E3 (ubiquitin ligase) and sub (substrate). The type of ubiquitin modification attached to the substrate dictates the function, activity, localization or even fate of the ubiquitinated protein.