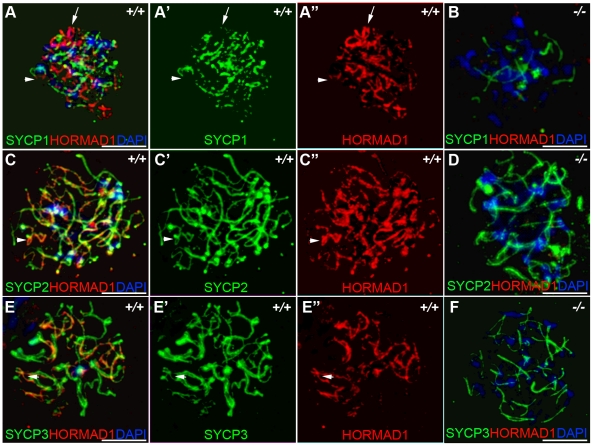
Figure 2. HORMAD1 co-localizes with SYCP2 and SYCP3, but not with SYCP1.
Chromosomal spread assay in wild-type (+/+) and Hormad1−/− (−/−) zygotene stage spermatocytes. (A–B) Immunofluorescence staining with anti-SYCP1 (Green) and anti-HORMAD1 (Red) antibody. HORMAD1 preferentially localizes to unsynapsed regions of chromosome axes (arrow head) and sex body (arrow) but does not co-localize with SYCP1 (A-A”). Hormad1 deficiency does not affect SYCP1 localization to the axes (B). HORMAD1 co-localizes with SYCP2 on the unsynapsed chromosome axes (C-C”), but HORMAD1 deficiency does not affect SYCP2 localization to the axes (D). SYCP3, another integral and critical component of the synaptonemal complex co-localizes with HORMAD1 on unsynapsed axes (E-E”). Similar to SYCP1 and SYCP2, SYCP3 localizes to the axes despite HORMAD1 deficiency (F). DNA was stained with DAPI. Scale bars: 10 µm.