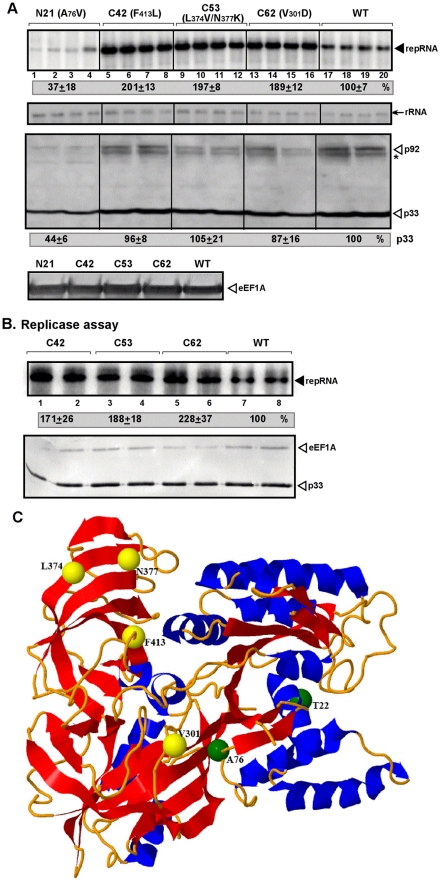
Figure 1. The effect of eEF1A mutations on TBSV repRNA accumulation in yeast.
(A) The yeast strains expressed only one form of eEF1A, as indicated. Top panel: Replication of the TBSV repRNA was measured by Northern blotting 24 h after initiation of TBSV replication. The accumulation level of repRNA was normalized based on the rRNA (middle panel, the 18S ribosomal RNA levels were estimated by Northern blotting). Bottom two panels: Accumulation of p33/p92pol and eEF1A was estimated by Western blotting using anti-His and anti-eEF1A antibody, respectively. Note that * marks an SDS-resistant p33 homodimer band. (B) An in vitro replicase assay to test the relative activity of the tombusvirus replicase obtained from yeast expressing various mutants of eEF1A. Top panel: We tested the in vitro replicase activity using comparable amounts of affinity-purified replicase with added DI-72 RI(−) RNA template. Bottom panels: Western blot analysis showing p33 viral replication protein and the co-purified eEF1A in the above purified replicase preparations. (C) Critical eEF1A residues for tombusvirus replication. Three novel mutants of eEF1A were identified, which exhibited increased tombusvirus replication (V301D, L374V/N377K, and F413L; yellow balls) while the new A76V and the previously identified T22S exhibited decreased tombusvirus replication (green balls). The structure of eEF1A was generated using Jmol with PDB coordinates 1IJE.