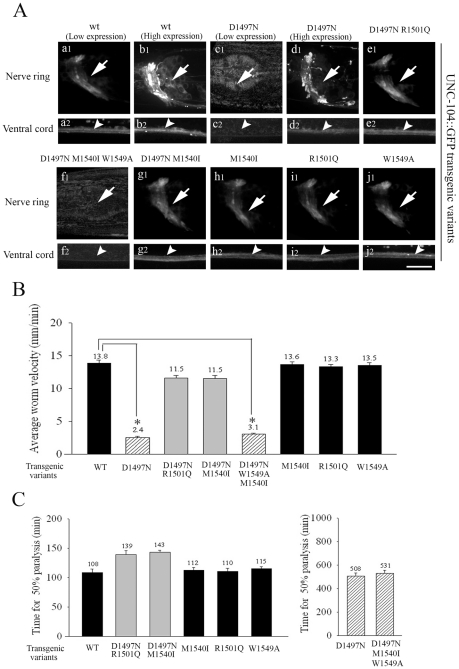
Figure 6. Localization and behavioural rescue of UNC-104::GFP transgenes with different PH domain mutations.
(A) Expression and localization of UNC-104::GFP PH domain variants in unc-104(e1265) background. All transgenic animals except those with the D1497N and D1497N M1540I W1549A mutations in the PH domain express GFP at high levels. Over-expression of UNC-104(D1497N)::GFP shows expression and localization of the protein similar to high copy number UNC-104::GFP transgenic animals. In all transgenes that show expression, the localization of UNC-104 is similar to wild type UNC-104::GFP. Scale bar: 10 µm. (B) Locomotory behaviour of unc-104(e1265) animals carrying various UNC-104::GFP transgenes. All transgenes except UNC-104(D1497N)::GFP (*p = 10-31) and UNC-104(D1497N M1540I W1549A)::GFP (*p = 10-29) rescue locomotry behaviour. While UNC-104(D1497N R1501Q)::GFP and UNC-104(D1497N M1540I)::GFP also provide rescue, they are significantly different from wild type (*p = 10-7, 10-6). UNC-104(D1497N) does rescue viability of the unc-104(rh142), a null allele (data not shown). All data represented as mean ± SEM. (C) Aldicarb resistance of unc-104(e1265) animals carrying various UNC-104::GFP transgenes. UNC-104(D1497N)::GFP (*p = 0.001) and UNC-104(D1497N M1540I W1549A)::GFP (*p = 0.007) animals are highly resistant to aldicarb and do not provide functional rescue. All other transgenes confer aldicarb resistance similar to wild type and provide functional rescue. All data represented as mean ± SEM.