Figure 1.
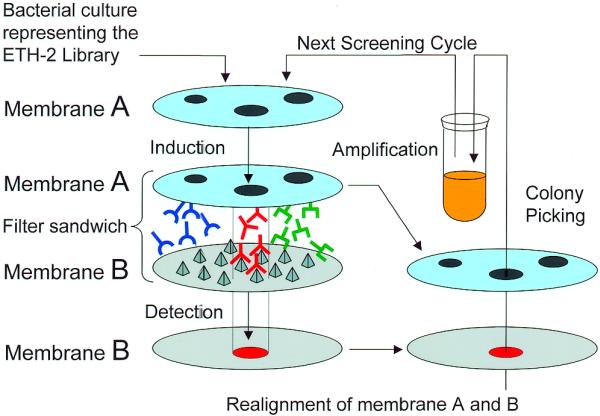
Schematic representation of the iterative colony screening method. Bacteria expressing a potentially different antibody fragment were spread on a Durapore filter membrane (A). On the filter, placed on a solid medium that represses expression of the antibody fragments, colonies were visible after 8 h incubation at 37°C (here three different colonies are depicted schematically). A second filter membrane (B) was coated with the antigen of interest (represented by pyramids), laid on a solid medium capable of inducing the expression of scFvs, and in contact with membrane A. Antibody fragments that diffused from membrane A and that bound to the antigen (in red) were captured on membrane B, and could be detected by an enzymatic colourimetric reaction. The corresponding colonies could be identified on membrane A, regrown and the procedure could be repeated until single positive colonies producing monoclonal antibodies were identified.
