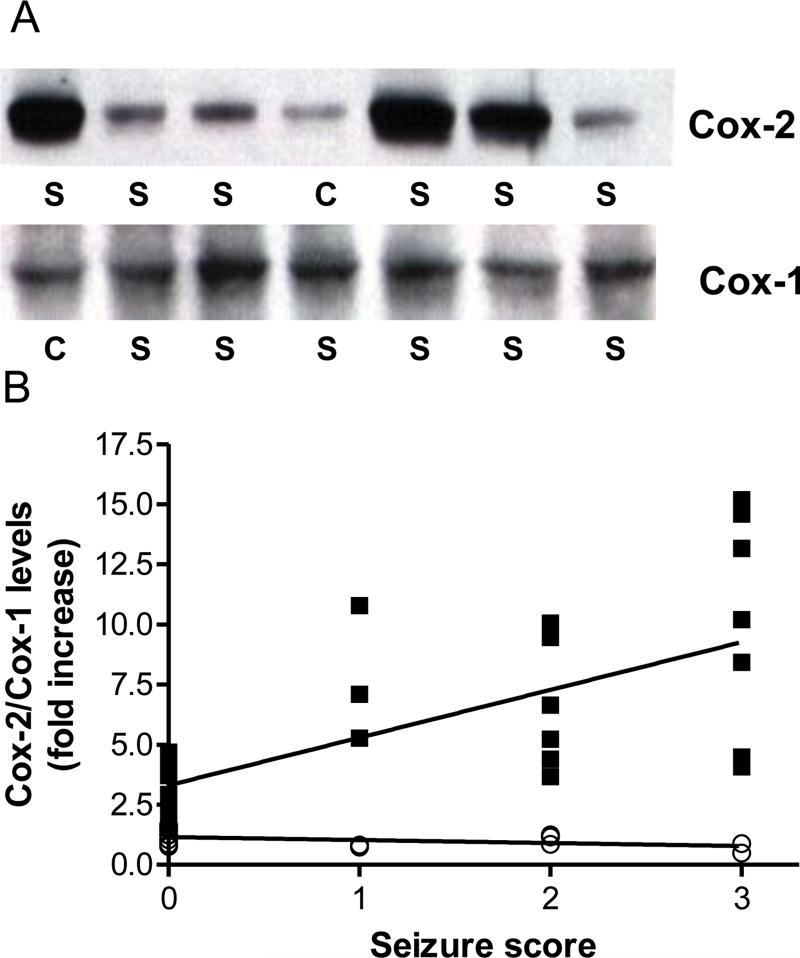
Fig 5.
Soman-induced increases in COX-2 expression are correlated with seizure intensity. Rats (N= 5-8 per group) were treated with soman and scored behaviorally for seizure intensity 1 hr after treatment as described in Materials and Methods. At 48 hr after soman, brains were processed for immunoblotting for COX-2 and COX-1 in the hippocampus. Panel A shows immunoblotting results for COX-2 and COX-1 from controls (C) and soman treated rats (S). The fold-increase in COX-2 (■) and COX-1 (○) expression caused by soman was plotted versus seizure intensity in panel B. The relationship between changes in COX-2 levels and seizure intensity was significant (r=0.73, p < 0.0001). COX-1 levels were not changed by soman treatment.