Figure 4.
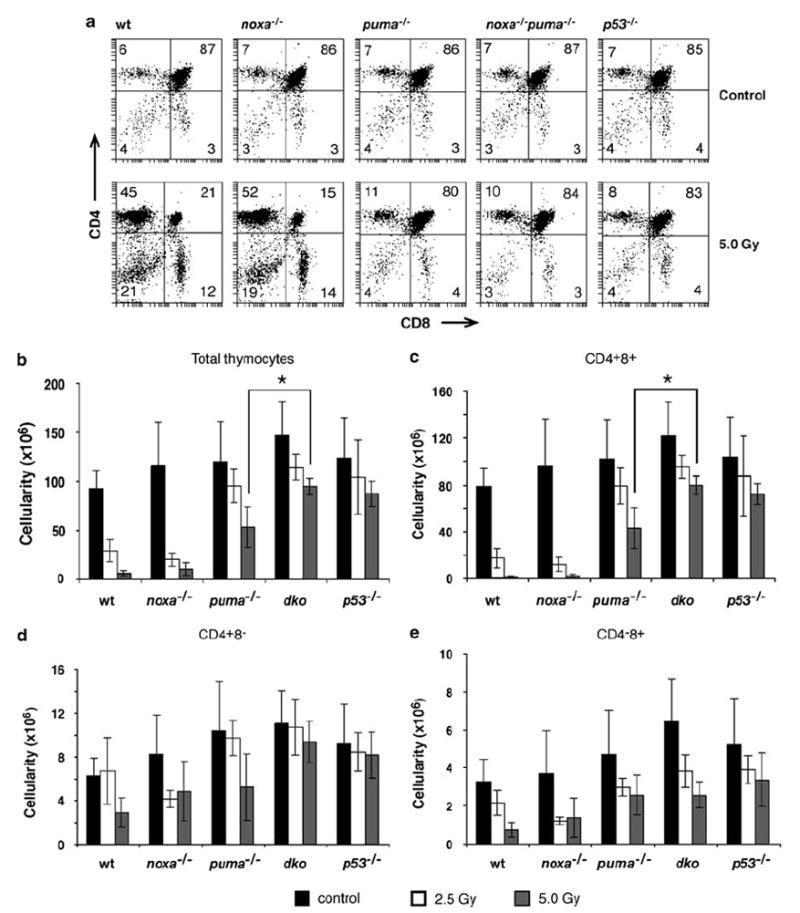
Sensitivity of thymocytes from noxa−/−puma−/− mice to γ-irradiation in vivo. Wt, noxa−/−, puma−/−, noxa−/−puma−/− or p53−/− mice were left untreated or exposed to 2.5 or 5 Gy full body γ-irradiation and the thymus was harvested 20 h later. (a) Representative dot plots of stained thymocytes from control or 5 Gy-irradiated mice of each genotype. Percentages of CD4−8−, CD4−8+ CD4+8− and CD4+8+ cells are indicated in the quadrants. (b) Thymic cellularity was determined for untreated or irradiated mice of each genotype. In (c), (d) and (e), the total number of thymocytes in the indicated subset was determined by multiplying the total thymic cellularity by the percentage of cells in that subset. Bars represent means±S.D. of 4–14 mice of each genotype per treatment in at least three independent experiments. Thymic cellularity and total number of CD4+8+ thymocytes remaining in noxa−/−puma−/− animals treated with 5 Gy γ-radiation was significantly greater than in puma−/− animals treated with the same dose (P<0.01)
