Figure 2.
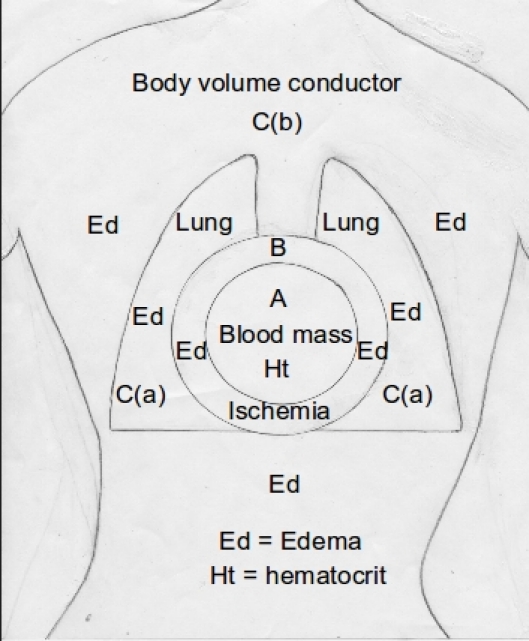
A 3-compartment model of HF, showing compartment A (intracardiac), which can be influenced by changes in the intracavitary blood mass and the hematocrit, compartment B (the heart), which can be influenced by edema and ischemia, and compartment C (body volume conductor), which includes the lungs [C(a)] and the rest of the body [C(b)], which can be influenced by edema; the separation of the lungs and the rest of the body is an analogy introduced to accommodate the clinical states of lung congestion [C(a)] and/or peripheral edema [C(b)].
