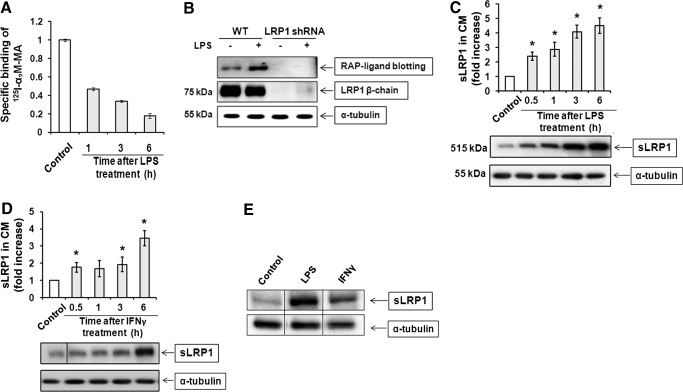
Figure 1. LPS and IFN-γ promote LRP1 shedding.
(A) RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in SFM and then treated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 1–6 h. Cell surface LRP1 was determined by measuring specific binding of methylamine-activated α2M (α2M-MA) at 4°C. (B) RAW 264.7 cells (WT) and cells in which LRP1 was silenced with shRNA were treated with 10 ng/ml LPS in SFM for 1 h or with vehicle. CM was recovered and subjected to RAP ligand blotting to detect sLRP1. The absence of sLRP1 in CM from cells in which LRP1 was silenced confirmed that our RAP ligand-blotting method is detecting sLRP1 specifically. (C) RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in SFM for 1 h and then challenged with 10 ng/ml LPS in SFM for the indicated times. sLRP1 in the medium was determined by RAP ligand blotting (mean±sem; n=3). For each well, cell extracts were prepared and subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect α-tubulin as a control for the number of cells in each well. (D) RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in SFM for 1 h and then treated with IFN-γ (25 ng/ml) in SFM. sLRP1 levels were determined in CM by RAP ligand blotting. Cell extracts were immunoblotted to detect α-tubulin. (C and D) The relative levels of sLRP1 were determined by comparison with CM from control cells that were incubated in the absence of stimulant for 6 h. *P<0.05. (E) Primary cultures of BMMs were treated with LPS (10 ng/ ml) or IFN-γ (25 ng/ml) for 3 h. sLRP1 was determined in CM. α-Tubulin was determined in cell extracts. The presented study is representative of 3 separate replicates.