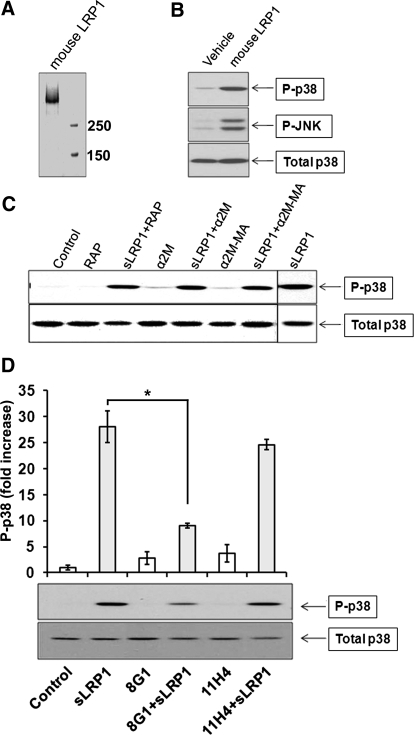
Figure 5. Characterization of sLRP1-initiated cell signaling.
(A) Coomassie-stained gel showing purified mouse LRP1. (B) RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in SFM for 1 h and then treated with purified mouse LRP1 (50 nM), rat LRP1 (50 nM), or vehicle. Immunoblot analysis was performed to assess cell signaling. (C) RAW 264.7 cells were treated for 20 min with sLRP1 (50 nM), sLRP1 that was preincubated with RAP (250 nM), native α2M that does not bind to sLRP1 (100 nM), sLRP1 (50 nM) that was preincubated with native α2M (100 nM), methylamine-activated α2M (100 nM), and methylamine-activated α2M (100 nM) that was preincubated with sLRP1 (50 nM). Immunoblot analysis was performed to detect phospho-p38 MAPK and total p38 MAPK. (D) sLRP1 (50 nM) was preincubated with a 50-fold molar excess of antibody 8G1 or 11H4 or with vehicle. Cells were treated with the preincubated sLRP1 or with the antibodies alone. Immunoblot analysis was performed to detect phospho-p38 MAPK and total p38 MAPK. All experiments were performed in triplicate. The studies shown in D were analyzed by densitometry. The bar graph shows the mean ± sem; *P<0.05.