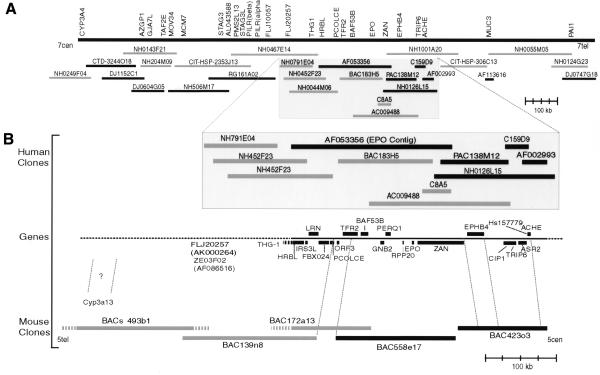
Figure 1.
Overview of the refined chromosome 7q22 physical map for the region spanning the genes PAI1 and CYP3A4, with a direct comparison with 640 kb of orthologous genomic sequence from mouse chromosome 5. Black rectangles represent completely sequenced regions, gray rectangles represent partially sequenced or PCR-mapped clones and gray hatches represent parts of clones whose overlapping distances are not known. (A) Representative genes and clones provide further refinement to the human gene map previously described (11). A minimal tiling path determined by hybridization, PCR and in silico methods clearly establishes MUC3 on the telomeric side of ACHE and links the HRBL end of AF053356 to the CYP3A4 locus (see http://www.genet.sickkids.on.ca/chromosome7/ for a more detailed physical map including additional genes, further clones and experimental details). (B) Comparative human–mouse genomic map showing conserved synteny of at least 22 genes. The composite gene map shows human genes (upper case letters), all of which have a mouse ortholog, as well as the mouse gene Cyp3a13, whose human ortholog is yet to be determined. The orientation of the mouse BAC clones in relation to chromosome 5 was inferred from the location of the mouse Cyp3a gene locus on a refined chromosome 5 map (http://genome.nhgri.nih.gov/chr7/comparative; 8). PCR mapping determined that a TSC-22-like gene, THG-1, is next to HRBL in both human and mouse followed by ZE03F02 and FLJ20257 (Ze03f02 and D5Wsu46e) whose order has not yet been determined. None of the genes shown between FLJ20257 and CYP3A4 has been identified in our partial mouse sequence data for BACs 139n8 and 493b1 (D5Wsu46e to Cyp3a13).