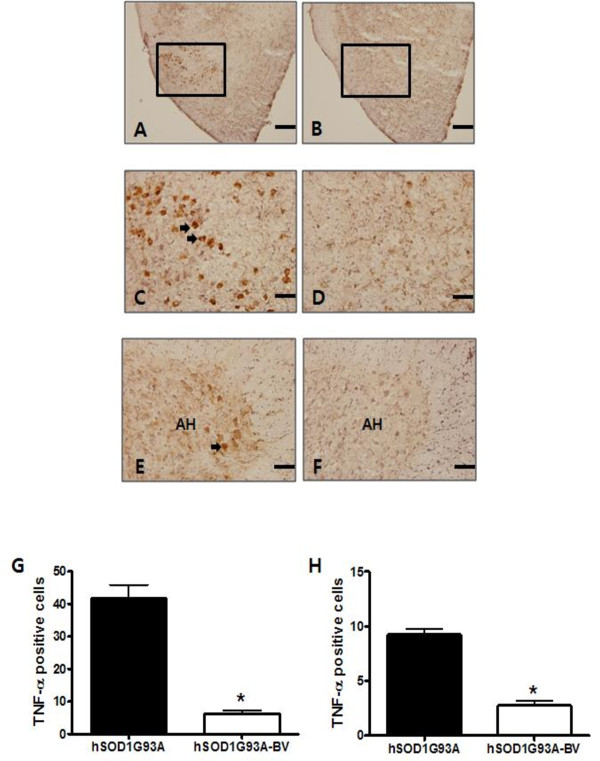
Figure 5.
Immunohistochemical study of TNF-α in the brainstem and anterior horns of the lumbar (L4) spinal cord in BV- or saline-treated familial mutant SOD1 mice. TNF-α IR is significantly reduced in the facial nucleus of the brainstem from BV-treated hSOD1G93A mice (A, B). Scale bars = 400 μm (A, B). High magnification of boxes (facial nucleus) in A and B (C, D). In the anterior horn of the spinal cord, the number of TNF-α-immunoreactive cells was increased in hSOD1G93A mice, but it was reduced by treatment with BV (E, F). Scale bars = 100 μm (C-F). Cell counting for TNF-α immunoreactive cells in saline- (black columns, n = 3) or BV-treated (white columns, n = 4) hSOD1G93A mice (G, H). BV treatment reduced significantly TNF-a immunoreactivity in the brainstem (G) and lumbar spinal cord (H). Data were analyzed with a t-test. *p < 0.001. AH: anterior horn